Anticancer Effect of Cycas media: Molecular Basis Through Modulation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 39519654
- PMCID: PMC11547819
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29215013
Anticancer Effect of Cycas media: Molecular Basis Through Modulation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway
Abstract
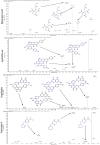
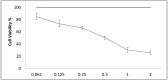
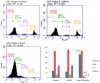
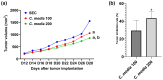
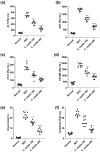
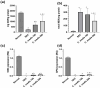
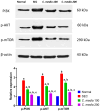
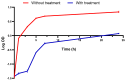
Many researchers are focusing on screening the biological activities of plants owing to their safety and possible pharmacological actions. Consequently, we aimed to explore the antiproliferative and cytotoxic properties of Cycas media methanolic extract on HepG2 cell lines. Moreover, we also explore the antitumor action against the experimentally induced solid Ehrlich carcinoma (SEC) model and investigate the possible involved molecular mechanisms. Also, the antibacterial action of the extract was elucidated. Different concentrations of the extract were incubated with HepG2 to determine cytotoxicity, followed by cell cycle analysis. The in vivo experiment was accomplished by grouping the animals into four different groups (n = 10); normal control, SEC, C. media 100, and C. media 200. The extract was administered at 100 and 200 mg/kg. Tumor volume, tumor inhibition rate, toxicity profile, and antioxidant biomarkers were determined. Moreover, the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway was investigated as a possible underlying antitumor mechanism. The tumor control group showed a remarkable upregulation for PI3K, p-AKT, and p-mTOR, along with downregulation for the antioxidant SOD and GPX4, as well as decreased levels of GSH and MDA. C. media extract reversed these parameters to a significant level and the higher dose showed a superior antitumor effect. C. media extract showed antiproliferative effects against HepG2 cells, along with a suppressive action on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and an antioxidant effect. Additionally, C. media had antibacterial consequences against S. aureus isolates with minimum inhibitory concentrations from 32 to 128 µg/mL. It also caused a noteworthy growth delay as well as a notable reduction in the membrane integrity of S. aureus isolates. These beneficial outcomes suggest C. media to have potential antitumor and antibacterial activities.
Keywords: Cycas media; EAC; HepG2; PI3K/AKT/mTOR; Staphylococcus aureus; antitumor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chloroform extract from Sophora Tonkinensis Gagnep. inhibit proliferation, migration, invasion and promote apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by silencing the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 May 10;271:113879. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113879. Epub 2021 Jan 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33524509
-
Zanthoxylum bungeanum Seed Oil Elicits Autophagy and Apoptosis in Human Laryngeal Tumor Cells via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(18):2610-2619. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666210401103820. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33797380
-
Total saponins of Bolbostemma paniculatum (maxim.) Franquet exert antitumor activity against MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells via inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Nov 8;19(1):304. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2708-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31703679 Free PMC article.
-
Promising Anticancer Activities of Alismatis rhizome and Its Triterpenes via p38 and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathways.Nutrients. 2021 Jul 18;13(7):2455. doi: 10.3390/nu13072455. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34371964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multifaceted anticancer potential of luteolin: involvement of NF-κB, AMPK/mTOR, PI3K/Akt, MAPK, and Wnt/β-catenin pathways.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Feb;33(2):505-525. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01596-8. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39543054 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

