Keep Your TEMPO Up: Nitroxide Radicals as Sensors of Intermolecular Interactions
- PMID: 39519672
- PMCID: PMC11548018
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29215032
Keep Your TEMPO Up: Nitroxide Radicals as Sensors of Intermolecular Interactions
Abstract
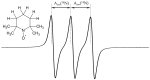
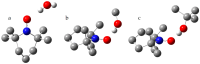
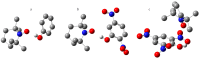
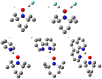
This study examines experimental data on the influence of the surrounding medium and non-covalent interactions on the isotropic hyperfine coupling constant, Aiso(14N), of the stable nitroxide radical 2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl)oxyl (TEMPO) in solution. The data were used to identify a density functional theory functional/basis set combination that accurately reproduces the experimental Aiso(14N) values. The variations in Aiso(14N) due to external factors are two orders of magnitude greater than the accuracy of its experimental measurements, making Aiso(14N) a highly sensitive experimental probe for quantifying these effects. Additionally, it was found that the proton-accepting ability of the N-O• moiety in TEMPO resembles that of the P=O moiety, enabling the simultaneous formation of two equally strong hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: EPR; TEMPO; hydrogen bonding; hyperfine coupling constant; non-covalent interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nitroxide/substrate weak hydrogen bonding: attitude and dynamics of collisions in solution.J Am Chem Soc. 2007 Jun 6;129(22):7018-27. doi: 10.1021/ja064632i. Epub 2007 May 12. J Am Chem Soc. 2007. PMID: 17497854
-
Nitroxide radicals as hydrogen bonding acceptors. An infrared and EPR study.Chemphyschem. 2002 Sep 16;3(9):789-93. doi: 10.1002/1439-7641(20020916)3:9<789::AID-CPHC789>3.0.CO;2-Z. Chemphyschem. 2002. PMID: 12436906
-
1,2,3-propanetriol radicals formed during oxidative stress.Magn Reson Chem. 2019 Apr;57(4):S95-S100. doi: 10.1002/mrc.4822. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Magn Reson Chem. 2019. PMID: 30586474
-
Computational analysis of substituent effects on proton affinity and gas-phase basicity of TEMPO derivatives and their hydrogen bonding interactions with water molecules.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 10;14(1):8434. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58582-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38600208 Free PMC article.
-
To be a radical or not to be one? The fate of the stable nitroxide radical TEMPO [(2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidin-1-yl)oxyl] undergoing plasma polymerization into thin-film coatings.Biointerphases. 2020 Jun 26;15(3):031015. doi: 10.1116/6.0000259. Biointerphases. 2020. PMID: 32590900
Cited by
-
Editorial to the Special Issue "Gulliver in the Country of Lilliput: An Interplay of Noncovalent Interactions (Volume II)".Molecules. 2025 Jul 15;30(14):2972. doi: 10.3390/molecules30142972. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40733237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vega S. Dynamic Nuclear Polarization with or without Spin Diffusion? Online Lect. 2011. [(accessed on 7 October 2024)]. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-7xu7a0YQy4.
-
- Asanbaeva N.B., Dobrynin S.A., Morozov D.A., Haro-Mares N., Gutmann T., Buntkowsky G., Bagryanskaya E.G. An EPR Study on Highly Stable Nitroxyl-Nitroxyl Biradicals for Dynamic Nuclear Polarization Applications at High Magnetic Fields. Molecules. 2023;28:1926. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041926. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Herr K., Fleckenstein M., Brodrecht M., Höfler M.V., Heise H., Aussenac F., Gutmann T., Reggelin M., Buntkowsky G. A novel strategy for site selective spin-labeling to investigate bioactive entities by DNP and EPR spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:13714. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92975-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

