Anticonvulsant, Anticholinesterase and Cytoprotective Effects of the Aqueous Extract of Lippia sidoides Cham
- PMID: 39519956
- PMCID: PMC11548531
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13213034
Anticonvulsant, Anticholinesterase and Cytoprotective Effects of the Aqueous Extract of Lippia sidoides Cham
Abstract
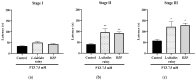
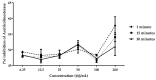
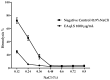
(1) Background: Lippia sidoides Cham is a Brazilian aromatic plant rich in phenolic compounds. In traditional medicine, its leaves are used to treat diseases of the Central Nervous System such as stress and anxiety. This study evaluates the capacity of the aqueous extract of L. sidoides as an anticonvulsant, anticholinesterase and antihemolytic agent. (2) Methods: The extract was obtained from the leaves using water as a solvent, then dried in a spray dryer. The anticonvulsant effect was evaluated in zebrafish models using the pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) method. The anticholinesterase effect was determined using the acetylcholinesterase enzyme and physostigmine as a positive control. The antihemolytic action was evaluated by exposing erythrocytes to different concentrations of NaCl in the presence and absence of the extract. (3) Results: The anticonvulsant effect was observed at a concentration of 400 mg/kg, delaying convulsive crises. In the anticholinesterase assay, a dose-dependent action and variation in the effect over time were observed, demonstrating a reversible effect of the extract. For the osmotic fragility test, the extract showed satisfactory results, providing cellular protection across all variations of NaCl concentration. (4) Conclusions: These results demonstrate the promising potential of L. sidoides extract for the development of drugs that act in the treatment of diseases that affect the Central Nervous System.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; antihemolytic effect; aqueous extract; epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis toxicity by different methods and anxiolytic effect of the aqueous extract Lippia sidoides Cham.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 30;12(1):20626. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23999-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36450779 Free PMC article.
-
Essential Oil Composition, Antimicrobial and Pharmacological Activities of Lippia sidoides Cham. (Verbenaceae) From São Gonçalo do Abaeté, Minas Gerais, Brazil.Pharmacogn Mag. 2016 Oct-Dec;12(48):262-270. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.192197. Pharmacogn Mag. 2016. PMID: 27867267 Free PMC article.
-
Prospection of Enzyme Modulators in Aqueous and Ethanolic Extracts of Lippia sidoides Leaves: Genotoxicity, Digestion, Inflammation, and Hemostasis.Chem Biodivers. 2019 Mar;16(3):e1800558. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201800558. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Chem Biodivers. 2019. PMID: 30600918
-
General Characteristics, Phytochemistry and Pharmacognosy of Lippia sidoides.Nat Prod Commun. 2015 Nov;10(11):1861-7. Nat Prod Commun. 2015. PMID: 26749814 Review.
-
A Systematic Review of the Potential Effects of Lippia sidoides on Dental Plaque and Periodontal Diseases.Planta Med. 2022 Apr;88(5):341-355. doi: 10.1055/a-1554-6947. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Planta Med. 2022. PMID: 34598290
References
-
- Sasikumar P., Aswathy M., Tripathi Prem P., Vasu Radhakrishnan K., Chakrapani P.S.B. Plant derived bioactive compounds and their potential to enhance adult neurogenesis. Phytomed. Plus. 2022;2:100191. doi: 10.1016/j.phyplu.2021.100191. - DOI
-
- Matos F.J.A. Plantas medicinais: Guia de Seleção e Emprego de Plantas Usadas em Fitoterapia no Nordeste do Brasil. IU; Fortaleza, Brazil: 2007. 394p
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

