Minimally Invasive Syringe-Injectable Hydrogel with Angiogenic Factors for Ischemic Stroke Treatment
- PMID: 39520382
- PMCID: PMC11874675
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202403119
Minimally Invasive Syringe-Injectable Hydrogel with Angiogenic Factors for Ischemic Stroke Treatment
Abstract
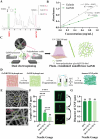
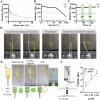
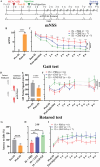
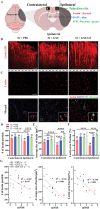
Ischemic stroke (IS) accounts for most stroke incidents and causes intractable damage to brain tissue. This condition manifests as diverse aftereffects, such as motor impairment, emotional disturbances, and dementia. However, a fundamental approach to curing IS remains unclear. This study proposes a novel approach for treating IS by employing minimally invasive and injectable jammed gelatin-norbornene nanofibrous hydrogels (GNF) infused with growth factors (GFs). The developed GNF/GF hydrogels are administered to the motor cortex of a rat IS model to evaluate their therapeutic effects on IS-induced motor dysfunction. GNFs mimic a natural fibrous extracellular matrix architecture and can be precisely injected into a targeted brain area. The syringe-injectable jammed nanofibrous hydrogel system increased angiogenesis, inflammation, and sensorimotor function in the IS-affected brain. For clinical applications, the biocompatible GNF hydrogel has the potential to efficiently load disease-specific drugs, enabling targeted therapy for treating a wide range of neurological diseases.
Keywords: angiogenesis; electrospinning; gelatin‐norbornene; ischemic stroke; sensorimotor function.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Healthcare Materials published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simultaneous nano- and microscale structural control of injectable hydrogels via the assembly of nanofibrous protein microparticles for tissue regeneration.Biomaterials. 2019 Dec;223:119458. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119458. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Biomaterials. 2019. PMID: 31491598
-
Sliding Fibers: Slidable, Injectable, and Gel-like Electrospun Nanofibers as Versatile Cell Carriers.ACS Nano. 2016 Mar 22;10(3):3282-94. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b06605. Epub 2016 Feb 24. ACS Nano. 2016. PMID: 26885937
-
Injectable thermo-responsive Poloxamer hydrogel/methacrylate gelatin microgels stimulates bone regeneration through biomimetic programmed release of SDF-1a and IGF-1.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jun;271(Pt 2):132742. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132742. Epub 2024 May 30. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38821297
-
Injectable gelatin derivative hydrogels with sustained vascular endothelial growth factor release for induced angiogenesis.Acta Biomater. 2015 Feb;13:88-100. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.11.002. Epub 2014 Nov 8. Acta Biomater. 2015. PMID: 25462840 Free PMC article.
-
Highly angiogenic peptide nanofibers.ACS Nano. 2015 Jan 27;9(1):860-8. doi: 10.1021/nn506544b. Epub 2015 Jan 13. ACS Nano. 2015. PMID: 25584521 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Region-specific brain decellularized extracellular matrix promotes cell recovery in an in vitro model of stroke.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 7;15(1):11921. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95656-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40195414 Free PMC article.
-
A review: Carrier-based hydrogels containing bioactive molecules and stem cells for ischemic stroke therapy.Bioact Mater. 2025 Mar 5;49:39-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.01.014. eCollection 2025 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40124600 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tsao C. W., Aday A. W., Almarzooq Z. I., Anderson C. A. M., Arora P., Avery C. L., Baker‐Smith C. M., Beaton A. Z., Boehme A. K., Buxton A. E., Commodore‐Mensah Y., Elkind M. S. V., Evenson K. R., Eze‐Nliam C., Fugar S., Generoso G., Heard D. G., Hiremath S., Ho J. E., Kalani R., Kazi D. S., Ko D., Levine D. A., Liu J., Ma J., Magnani J. W., Michos E. D., Mussolino M. E., Navaneethan S. D., Parikh N. I., et al., Circulation 2023, 147, e93. - PubMed
-
- Kumar S., Selim M. H., Caplan L. R., Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 105. - PubMed
-
- Catanese L., Tarsia J., Fisher M., Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 541. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

