Dapagliflozin targets SGLT2/SIRT1 signaling to attenuate the osteogenic transdifferentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 39520538
- PMCID: PMC11550308
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-024-05486-8
Dapagliflozin targets SGLT2/SIRT1 signaling to attenuate the osteogenic transdifferentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
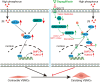
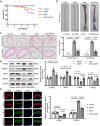
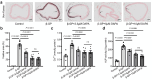
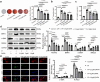
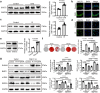
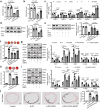
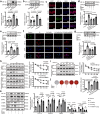
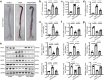
Vascular calcification is a complication that is frequently encountered in patients affected by atherosclerosis, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease (CKD), and that is characterized by the osteogenic transdifferentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). At present, there remains a pressing lack of any effective therapies that can treat this condition. The sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor dapagliflozin (DAPA) has shown beneficial effects in cardiovascular disease. The role of this inhibitor in the context of vascular calcification, however, remains largely uncharacterized. Our findings revealed that DAPA treatment was sufficient to alleviate in vitro and in vivo osteogenic transdifferentiation and vascular calcification. Interestingly, our study demonstrated that DAPA exerts its anti-calcification effects on VSMCs by directly targeting SGLT2, with the overexpression of SGLT2 being sufficient to attenuate these beneficial effects. DAPA was also able to limit the glucose levels and NAD+/NADH ratio in calcified VSMCs, upregulating sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) in a caloric restriction (CR)-dependent manner. The SIRT1-specific siRNA and the SIRT1 inhibitor EX527 attenuated the anti-calcification effects of DAPA treatment. DAPA was also to drive SIRT1-mediated deacetylation and consequent degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α). The use of cobalt chloride and proteasome inhibitor MG132 to preserve HIF-1α stability mitigated the anti-calcification activity of DAPA. These analyses revealed that the DAPA/SGLT2/SIRT1 axis may therefore represent a viable novel approach to treating vascular calcification, offering new insights into how SGLT2 inhibitors may help prevent and treat vascular calcification.
Keywords: Calorie restriction; Dapagliflozin; SGLT2; SIRT1; Vascular calcification.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors attenuate vascular calcification by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum protein thioredoxin domain containing 5 dependent osteogenic reprogramming.Redox Biol. 2024 Jul;73:103183. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103183. Epub 2024 May 13. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38759418 Free PMC article.
-
Intermedin1-53 attenuates aging-associated vascular calcification in rats by upregulating sirtuin 1.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Mar 31;12(7):5651-5674. doi: 10.18632/aging.102934. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32229709 Free PMC article.
-
Emodin-induced ERα degradation via SYVN1 alleviates vascular calcification by preventing HIF-1α deacetylation in chronic kidney disease.Phytomedicine. 2025 Sep;145:156915. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156915. Epub 2025 Jun 6. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40541127
-
Sirtuin-1 and Its Relevance in Vascular Calcification.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 26;21(5):1593. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051593. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32111067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 21; review on its participation in vascular calcification pathology.Vascul Pharmacol. 2020 Feb-Mar;125-126:106636. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2019.106636. Epub 2019 Dec 24. Vascul Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31881276 Review.
Cited by
-
Canagliflozin ameliorates high-salt-induced renal injury and premature aging in male Dahl salt-sensitive rats, with associated changes in SIRT6/HIF-1α signaling.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2546624. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2546624. Epub 2025 Aug 12. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40796808 Free PMC article.
-
Danlian-Tongmai formula improves diabetic vascular calcification by regulating CCN3/NOTCH signal axis to inhibit inflammatory reaction.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 6;15:1510030. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1510030. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39834821 Free PMC article.
-
Canagliflozin improves high-salt-induced aortic arteriosclerosis and premature aging in dahl salt-sensitive rats through the SIRT6/HIF-1 α signaling pathway.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jun 2. doi: 10.1007/s11010-025-05321-z. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40455355
References
-
- Rogers MA, Aikawa E (2019) Cardiovascular calcification: artificial intelligence and big data accelerate mechanistic discovery. Nat Rev Cardiol 16:261–274. 10.1038/s41569-018-0123-8 - PubMed
-
- Giachelli CM (2004) Mechanisms of vascular calcification in uremia. Semin Nephrol 24:401–402 - PubMed
-
- Chen Y et al (2022) Nidogen-2 is a Novel Endogenous Ligand of LGR4 to Inhibit Vascular Calcification. Circul Res 131:1037–1054. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321614 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

