Asparaginase and isoaspartyl peptidase 1 RNA interference suppresses the growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- PMID: 39520610
- PMCID: PMC11550296
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01228-1
Asparaginase and isoaspartyl peptidase 1 RNA interference suppresses the growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
Abstract
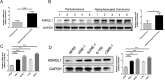
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is one of the common malignant tumors, and its pathogenesis has not been fully clarified. This study aims to explore the impact of RNA interference on the growth and invasion of NPC cells. Asparaginase and isoaspartyl peptidase 1 (ASRGL1)-short hairpin(sh) RNA expressing lentivirus was used to investigate the effect of ASRGL1 knockdown on NPC cells (C666-1 and SUN-1). The target shASRGL1 gene was determined by mRNA and protein expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells; nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation viability, migration, invasion, apoptosis, ATP levels, and oxidative stress were examined. The results found that ASRGL1 was found to be highly expressed in NPC tissues and cell lines. shASRGL1 exhibited a high gene expression knockdown efficiency, downregulated the ASRGL1 protein expression in the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, suppressed proliferation viability of transfected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, inhibited their migration and invasion and ATP levels, promoted nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell apoptosis, ROS, and ferroptosis. shASRGL1 plays a role in protecting against NPC cell growth and invasion.
Keywords: Asparaginase and isoaspartyl peptidase 1; Nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell; RNA interference.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Single-cell transcriptomics and metabolomics reveal the potential role of ASRGL1 in metabolic reprogramming and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2025 Aug;185:106788. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2025.106788. Epub 2025 May 2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40320045
-
Function of AXL and molecular mechanisms in regulation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Jun 28;47(6):685-697. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.210786. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 35837768 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Lentivirus-mediated RNAi knockdown of LMP2A inhibits the growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line C666-1 in vitro.Gene. 2014 May 25;542(1):77-82. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.03.020. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24630965
-
[YAP1 knockdown suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019 Mar 30;39(3):286-291. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.03.05. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31068306 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
KAI1 overexpression promotes apoptosis and inhibits proliferation, cell cycle, migration, and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.Am J Otolaryngol. 2017 Sep-Oct;38(5):511-517. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2016.09.011. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Am J Otolaryngol. 2017. PMID: 28583320
References
-
- Bray F, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Lin J-C. Adjuvant chemotherapy in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma based on plasma EBV load. J Radiat Oncol. 2012;1:117–27.
-
- Chen Y, et al. Progress report of a randomized trial comparing long-term survival and late toxicity of concurrent chemoradiotherapy with adjuvant chemotherapy versus radiotherapy alone in patients with stage III to IVB nasopharyngeal carcinoma from endemic regions of China. Cancer. 2013;119(12):2230–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
