A unique symbiosome in an anaerobic single-celled eukaryote
- PMID: 39521804
- PMCID: PMC11550330
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54102-7
A unique symbiosome in an anaerobic single-celled eukaryote
Abstract
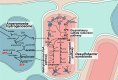
Symbiotic relationships between eukaryotes and prokaryotes played pivotal roles in the evolution of life and drove the emergence of specialized symbiotic structures in animals, plants and fungi. The host-evolved symbiotic structures of microbial eukaryotes - the vast majority of such hosts in nature - remain largely unstudied. Here we describe highly structured symbiosomes within three free-living anaerobic protists (Anaeramoeba spp.). We dissect this symbiosis using complete genome sequencing and transcriptomics of host and symbiont cells coupled with fluorescence in situ hybridization, and 3D reconstruction using focused-ion-beam scanning electron microscopy. The emergence of the symbiosome is underpinned by expansion of gene families encoding regulators of membrane trafficking and phagosomal maturation and extensive bacteria-to-eukaryote lateral transfer. The symbionts reside deep within a symbiosomal membrane network that enables metabolic syntrophy by precisely positioning sulfate-reducing bacteria alongside host hydrogenosomes. Importantly, the symbionts maintain connections to the Anaeramoeba plasma membrane, blurring traditional boundaries between ecto- and endosymbiosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Fronk, D. C. & Sachs, J. L. Symbiotic organs: the nexus of host–microbe evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol.37, 599–610 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Roth, L. E., Jeon, K. & Stacey, G. Homology in endosymbiotic systems: the term “symbiosome’. In Molecular Genetics of Plant-Microbe Interactions 220–225 (APS Press, St Paul, Minnesota).
-
- Husnik, F. et al. Bacterial and archaeal symbioses with protists. Curr. Biol.31, R862–R877 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Rotterová, J., Edgcomb, V. P., Čepička, I. & Beinart, R. Anaerobic ciliates as a model group for studying symbioses in oxygen‐depleted environments. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 69, e12912 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Beinart, R. A., Beaudoin, D. J., Bernhard, J. M. & Edgcomb, V. P. Insights into the metabolic functioning of a multipartner ciliate symbiosis from oxygen‐depleted sediments. Mol. Ecol.27, 1794–1807 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 12188/Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation (Gordon E. and Betty I. Moore Foundation)
- 5782/Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation (Gordon E. and Betty I. Moore Foundation)
- 12188/Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation (Gordon E. and Betty I. Moore Foundation)
- 12188/Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation (Gordon E. and Betty I. Moore Foundation)
- RES0043758/Gouvernement du Canada | Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (Conseil de Recherches en Sciences Naturelles et en Génie du Canada)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

