Correlation analysis of landscape patterns and urban thermal environment in Kunming based on a panel data model
- PMID: 39521818
- PMCID: PMC11550819
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-78118-7
Correlation analysis of landscape patterns and urban thermal environment in Kunming based on a panel data model
Abstract
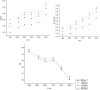
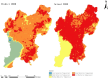
With the development of urbanization, the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of the urban landscape pattern play a decisive role in the intensity of the urban heat island (UHI) effect. A panel data model was constructed to study the relationship between the UHI effect and landscape pattern in Kunming from 1995 to 2020 at four different scales. The results indicate: (1) The landscape pattern of Kunming changed obviously with time, the artificial patch increased, the natural patch decreased, and the UHI effect became more and more obvious; (2) With an increase in scale, the number of influencing variables continues to grow, and the impact of artificial patches gradually intensifies; (3) The normalized difference water index (NDWI) has the greatest influence on the UHI, and the cooling effect is more obvious with the increase in scale. Unlike previous studies, the spatial configuration of the landscape in Kunming City had a stronger effect on the UHI effect than the landscape grouping and vegetation index; (4) This paper introduces the panel data model into the discussion of the UHI for the first time, providing a new method for better understanding the changing patterns of the urban thermal environment.
Keywords: Kunming; Landscape pattern; Panel data model; Urban heat island.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Voogt, J. A. & Oke, T. R. Thermal remote sensing of urban climates. Remote Sens. Environ.86, 370–384 (2003). - DOI
-
- Lowe, S. A. An energy and mortality impact assessment of the urban heat island in the US. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev.56, 139–144 (2016). - DOI
-
- He, B. J. et al. Perception, physiological and psychological impacts, adaptive awareness and knowledge, and climate justice under urban heat: A study in extremely hot-humid Chongqing, China. Sustainable Cities Soc.79, 103685 (2022). - DOI
Grants and funding
- YNWR-QNBJ-2019-064./Ten Thousand Talent Plans for Young Top-notch Talents of Yunnan Province
- YNWR-QNBJ-2019-064./Ten Thousand Talent Plans for Young Top-notch Talents of Yunnan Province
- YNWR-QNBJ-2019-064./Ten Thousand Talent Plans for Young Top-notch Talents of Yunnan Province
- YNWR-QNBJ-2019-064./Ten Thousand Talent Plans for Young Top-notch Talents of Yunnan Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

