Efficient PEGylated magnetic nanoniosomes for co-delivery of artemisinin and metformin: a new frontier in chemotherapeutic efficacy and cancer therapy
- PMID: 39521852
- PMCID: PMC11550824
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-78817-1
Efficient PEGylated magnetic nanoniosomes for co-delivery of artemisinin and metformin: a new frontier in chemotherapeutic efficacy and cancer therapy
Abstract
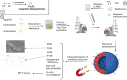
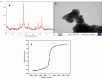
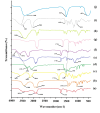
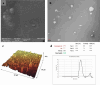
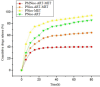
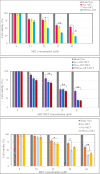
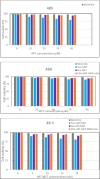
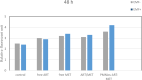
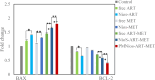
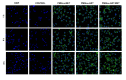
Two strategies were employed to modify the performance of the nano-niosome drug delivery system. Initially, the surface of the nano-niosomes underwent modification through the inclusion of polyethylene glycol, thereby altering its properties. Additionally, the core of the nano-niosomes was equipped with Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles to impart magnetic characteristics to the system. This study presents the development of PEGylated magnetic nanoniosomes (PMNios) for the co-delivery of artemisinin (ART) and metformin (MET) in cancer therapy, highlighting significant advancements in chemotherapeutic efficacy. The magnetization of the nano-niosomes facilitated the targeted delivery of drugs to specific tissues, while PEGylation improved the bioavailability of the nano-niosomes. These PEGylated magnetic niosomes (PMNios) were then loaded with artemisinin and metformin drugs. The synthesized PMNios were thoroughly evaluated in terms of zeta potential, size, morphology, and entrapment efficiency. The PMNios achieved a drug loading efficiency of 88%. They exhibited an average size of 298 nm, a polydispersity index of 0.32, and a zeta potential of - 19 mV, indicating the complete stability. SEM and TEM images of the PMNios revealed a spherical morphology. Subsequently, the PMNios were compared with other forms of nano-niosomes, including empty niosomes, non-magnetic niosomes, and non-PEGylated niosomes. The encapsulation of the nano-niosomes with magnetic nanoparticles allows for faster delivery of the encapsulated drugs to the tumor site, while PEGylation improved the stability, bioavailability, and controlled release of the PMNios. Furthermore, the in-vitro effectiveness of various formulations of the PMNios against A549, a lung cancer cell line, demonstrated that the PMNios exhibited appropriate toxicity towards cancer cell lines in the presence of an external magnetic field. Gene expression level of Bcl2 were lower for the PMNios-ART-MET system, whereas the level of Bax were higher than the other group. The PMNios-ART-MET system also demonstrated well internalization into the A549 cells and preponderant endocytosis. These findings underscore the novelty and potential of PMNios as a robust platform for the targeted co-delivery of hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs, promising a new frontier in cancer therapy by enhancing the therapeutic index and minimizing side effects.
Keywords: Artemisinin; Lung cancer; Magnetic noisome; Metformin; Targeted drug delivery system.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Co-delivery of artemisinin and metformin via PEGylated niosomal nanoparticles: potential anti-cancer effect in treatment of lung cancer cells.Daru. 2024 Jun;32(1):133-144. doi: 10.1007/s40199-023-00495-7. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Daru. 2024. PMID: 38168007 Free PMC article.
-
Design and optimization various formulations of PEGylated niosomal nanoparticles loaded with phytochemical agents: potential anti-cancer effects against human lung cancer cells.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Apr;75(2):442-455. doi: 10.1007/s43440-023-00462-8. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36859742
-
Exploring the potential of silymarin-loaded nanovesicles as an effective drug delivery system for cancer therapy: in vivo, in vitro, and in silico experiments.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Sep;397(9):7017-7036. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03099-3. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38630254
-
"Carnosine-Niosomal Delivery System for Targeted Cancer Therapy".Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Jun;83(2):1495-1520. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01626-w. Epub 2024 Dec 10. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39656368 Review.
-
Liposomes and Niosomes: New trends and applications in the delivery of bioactive agents for cancer therapy.Int J Pharm. 2025 Jan 5;668:124994. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124994. Epub 2024 Nov 24. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 39586512 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted apoptosis in breast cancer cells via niosome-mediated delivery of cyclophosphamide and sodium oxamate.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jan 18;52(1):139. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10241-8. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39827334
-
Artemisiae Annuae Herba: from anti-malarial legacy to emerging anti-cancer potential.Theranostics. 2025 Jun 20;15(15):7346-7377. doi: 10.7150/thno.115414. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40756346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vesicular Carriers for Phytochemical Delivery: A Comprehensive Review of Techniques and Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 2;17(4):464. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040464. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284459 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Witika, B. A., Bassey, K. E., Demana, P. H., Siwe-Noundou, X. & Poka, M. S. Investigating the use of niosomes in pharmaceuticals and drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Allied Sci.13, 85 (2024).
-
- Sharma, S., Garg, A., Agrawal, R., Chopra, H. & Pathak, D. A comprehensive review on niosomes as a tool for advanced drug delivery. Pharm. Nanatechnol.12, 206–228 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Javaid, S., Rana, T., Naeem, Z. & Sajid, N. Exploring niosomes: a comprehensive review of their structure, formulation, and biomedical applications. Currents Pharm. Res.2, 01–34 (2024).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

