Vitamin D has therapeutic effects on obesity and hyperandrogenemia in PCOS mouse model induced by low dose DHEA and high-fat diet
- PMID: 39521978
- PMCID: PMC11549824
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-024-03445-w
Vitamin D has therapeutic effects on obesity and hyperandrogenemia in PCOS mouse model induced by low dose DHEA and high-fat diet
Abstract
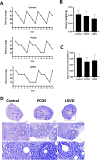
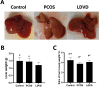
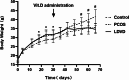
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the most complex and common reproductive endocrine disease among reproductive age women. This study aimed to investigate the effects of vitamin D (Vit.D) in a PCOS mouse model induced by low dose DHEA and high-fat diet. Prepubertal female mice were divided into 4 groups randomly: control, PCOS, PCOS with low dose Vit.D(LDVD), and PCOS with high dose Vit.D(HDVD) groups (n = 10 per group). PCOS mice were administrated with high-fat diet and subcutaneous injection with 6 mg/kg/day dehydroepiandrosterone throughout the study. After the first 30 days, 1,25(OH)2D3 was intend to be administered by intraperitoneal injection for 40 consecutive days, 1.3 µg/kg/week in LDVD group, and 13 µg/kg /week in HDVD group. However, the mice in HDVD group appeared to be fatigue and anorexic after the Vit.D injections, then all died within two weeks. The body weights and testosterone levels in PCOS group were significantly higher than those in the control and LDVD groups (P < 0.001). The total cholesterol levels in the control group were lower than those in PCOS and LDVD groups (P < 0.001). Further, the ratio of liver to body weight was different among groups (P < 0.001). Our data illustrates that Vit.D has therapeutic effects on obesity and hyperandrogenemia in PCOS mouse model induced by low dose DHEA and high-fat diet. However, over dose of Vit.D is toxic. Further researches are needed to elucidate the mechanisms.
Keywords: Hyperandrogenemia; Obesity; Polycystic ovary syndrome; Vitamin D.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2019-2-11/Fujian provincial health technology project
- 2021Y2012/Innovation Platform Project of Science and Technology,Fujian province
- 2021ZD01002/Key Project on Science and Technology Program of Fujian Health Commission
- 2022ZQNZD010/Major Scientific Research Program for Young and Middle-aged Health Professionals of Fujian Province,China
- 2023J011229/Fujian Natural Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

