Delayed Separation of Kaplan-Meier Curves is Commonly Observed in Studies of Advanced/Metastatic Solid Tumors Treated with Anti-PD-(L)1 Therapy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39522075
- PMCID: PMC11762587
- DOI: 10.1007/s11523-024-01108-2
Delayed Separation of Kaplan-Meier Curves is Commonly Observed in Studies of Advanced/Metastatic Solid Tumors Treated with Anti-PD-(L)1 Therapy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) Kaplan-Meier (KM) curves often show delayed survival benefit followed by long-term survival in a subgroup of patients. Such outcomes can violate the proportional hazards assumption, leading to a loss of statistical power.
Objective: We aimed to determine common trends in delayed separation to inform future ICI clinical trials.
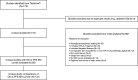
Patients and methods: A literature search was performed using Trialtrove® to identify phase III trials of antiprogrammed cell death (ligand)-1 (anti-PD-[L]1) agents in locally advanced/metastatic solid tumors published between January 2010 and September 2021. The frequency of delayed separation of overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) KM curves, correlation between duration of delayed separation in OS/PFS KM curves, and correlation between duration of delayed separation in OS/PFS KM curves with corresponding hazard ratios (HRs) were assessed in all-comer and PD-L1 enriched populations.
Results: Eighty-five studies with OS/PFS KM curves were identified. Most studies showed delayed separation of OS (> 67.9%) and PFS (> 54.5%) KM curves. The correlation between the duration of delayed separation in OS/PFS KM curves was strongest in the PD-L1 enriched population (adjusted R2 = 0.66). No correlation was seen between the duration of delayed separation of OS KM curves and OS HR. A modest correlation was seen between the duration of delayed separation of PFS KM curves and PFS HR in all-comer and PD-L1 enriched populations (adjusted R2 = 0.24 and 0.31, respectively).
Conclusions: Delayed separation of KM curves was common in clinical trials of anti-PD-(L)1 agents. Understanding delayed separation is key to clinical study designs and assessing outcomes with ICIs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Funding: Open Access funding enabled and organized by Seoul National University Hospital. Conflict of Interest: D.-Y.O. has received research funding from Array, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Eli Lilly, Handok, MSD, Novartis, and Servier, and consulting or advisory fees from Arcus Biosciences, ASLAN, AstraZeneca, Basilea, Bayer, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Genentech/Roche, Halozyme, IQVIA, Merck Serono, Novartis, Taiho, Turning Point, Yuhan, and Zymeworks. N.R. is an employee of and holds stock in AstraZeneca. M.Ż. is an employee of AstraZeneca. P.H. is an employee of and holds stock in Daiichi Sankyo. J.S. is an employee of and holds stock in AstraZeneca. M.L.J. has received research funding (to institution) from AbbVie, Acerta, Adaptimmune, Amgen, Apexigen, Arcus Biosciences, Array BioPharma, Artios Pharma, AstraZeneca, Atreca, BeiGene, BerGenBio, BioAlta, Black Diamond, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Calithera Biosciences, Carisma Therapeutics, Checkpoint Therapeutics, City of Hope National Medical Center, Corvus Pharmaceuticals, Curis, CytomX, Daiichi Sankyo, Dracen Pharmaceuticals, Dynavax, Elicio Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, EQRx, Erasca, Exelixis, Fate Therapeutics, Genentech/Roche, Genmab, Genocea Biosciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Gritstone Oncology, Guardant Health, Harpoon, Helsinn Healthcare SA, Hengrui Therapeutics, Hutchison MediPharma, IDEAYA Biosciences, IGM Biosciences, Immunitas Therapeutics, Immunocore, Incyte, Janssen, Jounce Therapeutics, Kadmon Pharmaceuticals, Kartos Therapeutics, Loxo Oncology, Lycera, Memorial Sloan Kettering, Merck, Merus, Mirati Therapeutics, Mythic Therapeutics, NeoImmune Tech, Neovia Oncology, Novartis, Numab Therapeutics, Nuvalent, OncoMed Pharmaceuticals, Palleon Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, PMV Pharmaceuticals, Rain Therapeutics, RasCal Therapeutics, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Relay Therapeutics, Revolution Medicines, Ribon Therapeutics, Rubius Therapeutics, Sanofi, Seven and Eight Biopharmaceuticals/Birdie Biopharmaceuticals, Shattuck Labs, Silicon Therapeutics, Stem CentRx, Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Tarveda, TCR2 Therapeutics, Tempest Therapeutics, Tizona Therapeutics, TMUNITY Therapeutics, Turning Point Therapeutics, University of Michigan, Vyriad, WindMIL Therapeutics, and Y-mAbs Therapeutics, and received consulting or advisory fees (to institution) from AbbVie, Amgen, Arcus Biosciences, Arrivent, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Axelia Oncology, Black Diamond, Calithera Biosciences, Daiichi Sankyo, EcoR1, Genentech/Roche, Genmab, Genocea Biosciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Gritstone Oncology, Ideaya Biosciences, Immunocore, iTeos, Janssen, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Mirati Therapeutics, Molecular Axiom, Novartis, Oncorus, Pyramid Biosciences, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Revolution Medicines, Sanofi-Aventis, SeaGen, Synthekine, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Turning Point Therapeutics, and VBL Therapeutics. Ethics Approval: Not applicable. Consent to Participate: Not applicable. Consent for Publication: Not applicable. Availability of Data and Material: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Code Availability: Not applicable. Author Contributions: N.R., J.S., M.Ż., and P.H. contributed to the study design and contributed to the acquisition and analysis of data. D.-Y.O. and N.R. supervised the study. All authors contributed to the interpretation of data, critically revised the manuscript, and provided final approval.
Figures



References
-
- Abou-Alfa GK, Lau G, Kudo M, Chan SL, Kelley RK, Furuse J, et al. Tremelimumab plus durvalumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. NEJM Evid. 2022;1:EVIDoa2100070. - PubMed
-
- Oh D-Y, He AR, Qin S, Chen L-T, Okusaka T, Vogel A, et al. Durvalumab plus gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced biliary tract cancer. NEJM Evid. 2022;1:EVIDoa2200015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

