The moderating effect of cardiometabolic factors on the association between hepatic and intrapancreatic fat
- PMID: 39523209
- PMCID: PMC11589540
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.24154
The moderating effect of cardiometabolic factors on the association between hepatic and intrapancreatic fat
Abstract
Objective: Previous studies have investigated the association between hepatic fat and intrapancreatic fat deposition (IPFD); however, results have been inconclusive. The presence of cardiometabolic factors in certain subpopulations could explain this discrepancy. The aim of the present study was to use moderation analyses to determine the conditions under which hepatic fat is associated with IPFD.
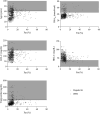
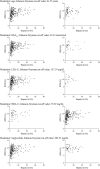
Methods: All participants underwent 3T abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and spectroscopy. Hepatic fat and IPFD were manually quantified by independent raters. Moderation analyses were performed with adjustment for sex and ethnicity.
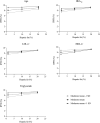
Results: There were 367 participants included. Adjusted analyses of the overall cohort revealed that age, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and triglycerides were significant moderators (p < 0.05) of the association between hepatic fat and IPFD. Ranges of significance included age < 61 years, HbA1c < 45 mmol/mol, LDL-C < 157 mg/dL, HDL-C > 36 mg/dL, and triglycerides < 203 mg/dL.
Conclusions: The association between hepatic fat and IPFD is generally present in young and middle-aged adults with good cardiometabolic health, whereas the link between the two fat depots becomes uncoupled in older adults or individuals with cardiometabolic risk factors.
© 2024 The Author(s). Obesity published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Obesity Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Obesity. World Obesity Atlas 2023. Published March 2, 2023. https://www.worldobesity.org/resources/resource-library/world-obesity-at...
-
- Koliaki C, Liatis S, Kokkinos A. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: revisiting an old relationship. Metabolism. 2019;92(3):98‐107. - PubMed
-
- Targher G, Day CP, Bonora E. Risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(14):1341‐1350. - PubMed
-
- Muzurović E, Peng CC, Belanger MJ, Sanoudou D, Mikhailidis DP, Mantzoros CS. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular disease: a review of shared cardiometabolic risk factors. Hypertension. 2022;79(7):1319‐1326. - PubMed
-
- Petrov MS, Taylor R. Intra‐pancreatic fat deposition: bringing hidden fat to the fore. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;19(3):153‐168. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

