The mutual interaction of TRPC5 channel with polycystin proteins
- PMID: 39523478
- PMCID: PMC11694000
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.24.265
The mutual interaction of TRPC5 channel with polycystin proteins
Abstract
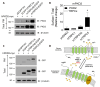
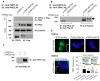
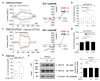
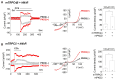
PKD1 regulates a number of cellular processes through the formation of complexes with the PKD2 ion channel or transient receptor potential classical (TRPC) 4 in the endothelial cells. Although Ca2+ modulation by polycystins has been reported between PKD1 and TRPC4 channel or TRPC1 and PKD2, the function with TRPC subfamily regulated by PKD2 has remained elusive. We confirmed TRPC4 or TRPC5 channel activation via PKD1 by modulating G-protein signaling without change in TRPC4/C5 translocation. The activation of TRPC4/C5 channels by intracellular 0.2 mM GTPγS was not significantly different regardless of the presence or absence of PKD1. Furthermore, the C-terminal fragment (CTF) of PKD1 did not affect TRPC4/C5 activity, likely due to the loss of the N-terminus that contains the G-protein coupled receptor proteolytic site (GPS). We also investigated whether TRPC1/C4/C5 can form a heterodimeric channel with PKD2, despite PKD2 being primarily retained in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Our findings show that PKD2 is targeted to the plasma membrane, particularly by TRPC5, but not by TRPC1. However, PKD2 did not coimmunoprecipitate with TRPC5 as well as with TRPC1. PKD2 decreased both basal and La3+-induced TRPC5 currents but increased M3R-mediated TRPC5 currents. Interestingly, PKD2 increased STAT3 phosphorylation with TRPC5 and decreased STAT1 phosphorylation with TRPC1. To be specific, PKD2 and TRPC1 compete to bind with TRPC5 to modulate intracellular Ca2+ signaling and reach the plasma membrane. This interaction suggests a new therapeutic target in TRPC5 channels for improving vascular endothelial function in polycystic kidney disease.
Keywords: Polycystic kidney disease 1 protein; Polycystic kidney disease 2 protein; Polycystic kidney diseases; Signal transducer and activator of transcription; Transient receptor potential canonical channel 5.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Potent, selective, and subunit-dependent activation of TRPC5 channels by a xanthine derivative.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Oct;176(20):3924-3938. doi: 10.1111/bph.14791. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31277085 Free PMC article.
-
Specific association of the gene product of PKD2 with the TRPC1 channel.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Mar 30;96(7):3934-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3934. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10097141 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction domains of transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC)1/4 and TRPC1/5 heteromultimeric channels.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Jun 3;474(3):476-481. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.04.138. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27131740
-
TRPC1 as a negative regulator for TRPC4 and TRPC5 channels.Pflugers Arch. 2019 Aug;471(8):1045-1053. doi: 10.1007/s00424-019-02289-w. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Pflugers Arch. 2019. PMID: 31222490 Review.
-
TRPC4 and TRPC5: receptor-operated Ca2+-permeable nonselective cation channels.Cell Calcium. 2003 May-Jun;33(5-6):441-50. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4160(03)00055-1. Cell Calcium. 2003. PMID: 12765689 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

