Sterile Alpha Motif Domain-Containing 5 Suppresses Malignant Phenotypes and Tumor Growth in Breast Cancer: Regulation of Polo-Like Kinase 1 and c-Myc Signaling in a Xenograft Model
- PMID: 39524172
- PMCID: PMC11550111
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.73259
Sterile Alpha Motif Domain-Containing 5 Suppresses Malignant Phenotypes and Tumor Growth in Breast Cancer: Regulation of Polo-Like Kinase 1 and c-Myc Signaling in a Xenograft Model
Abstract
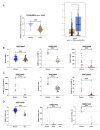
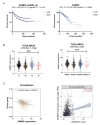
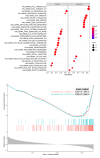
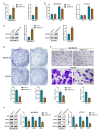
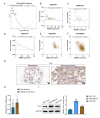
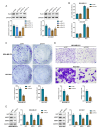
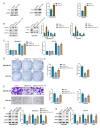
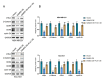
Background Breast cancer, particularly the triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) subtype, remains a significant clinical challenge due to its resistance to standard chemotherapy and high recurrence rate. In this study, we explored the role of Sterile Alpha Motif Domain-Containing 5 (SAMD5) as a potential regulatory partner with the c-Myc oncogenic signaling pathway in breast cancer. Materials and methods Functional assays were conducted to investigate the effects of SAMD5 overexpression on cell viability, colony formation, and invasive behavior in TNBC cell lines. This study further assessed the expression levels of proliferation and invasion markers, including Ki67 (a marker for cell proliferation), Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2), and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9). Mechanistic analyses identified a negative correlation between SAMD5 and Polo-like Kinase 1 (PLK1), a gene frequently overexpressed in breast cancer, particularly in TNBC. The effects of PLK1 knockdown on cell viability, colony formation, and invasion were observed, along with the impact of PLK1 overexpression on SAMD5's inhibitory activity. In vivo studies were performed using a xenograft tumor model in nude mice to evaluate the impact of SAMD5 overexpression on tumor weight and volume. Results SAMD5 overexpression significantly reduced cell viability, colony formation, and invasion in TNBC cells, and downregulated key proteins in the c-Myc signaling pathway, including c-Myc itself, β-catenin, Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4 (CDK4), Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 6 (CDK6), and Cyclin D1. PLK1 overexpression was found to counteract SAMD5's inhibitory effects. In vivo experiments demonstrated that SAMD5 overexpression led to a marked reduction in tumor weight and volume, effects that were partially reversed by PLK1 overexpression. Conclusions SAMD5 acts as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer, particularly in TNBC, by inhibiting critical cellular processes and downregulating the c-Myc signaling pathway. This effect appears to be mediated, in part, through its negative association with PLK1. Targeting the SAMD5/PLK1 axis offers a promising therapeutic strategy for addressing aggressive breast cancers.
Keywords: breast cancer; plk1; samd5; the c-myc signaling; triple-negative breast cancer.
Copyright © 2024, Tuo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. The Ethics Committee of the Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences and Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu, China issued approval TYL20210817. Animal subjects: Animal studies were performed following the Animal Research Reporting of In Vivo Experiments (ARRIVE) guidelines and were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences and Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu, China Issued protocol number TYL20210817. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Polo-like kinase 1: a potential therapeutic option in combination with conventional chemotherapy for the management of patients with triple-negative breast cancer.Cancer Res. 2013 Jan 15;73(2):813-23. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2633. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23144294
-
Calycosin inhibits triple-negative breast cancer progression through down-regulation of the novel estrogen receptor-α splice variant ER-α30-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2023 Sep;118:154924. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154924. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37393829
-
Small interfering RNA library screen identified polo-like kinase-1 (PLK1) as a potential therapeutic target for breast cancer that uniquely eliminates tumor-initiating cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Feb 6;14(1):R22. doi: 10.1186/bcr3107. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22309939 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the performance of polo-like kinase 1 in triple-negative breast cancer progression according to the centromere protein U-phosphorylation pathway.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 May 15;11(5):2142-2158. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34094674 Free PMC article.
-
DLC-3 suppresses cellular proliferation, migration, and invasion in triple-negative breast cancer by the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019 Apr 1;12(4):1224-1232. eCollection 2019. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31933937 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
