Impacts of low birthweight on kidney development and intergenerational growth of the offspring
- PMID: 39524353
- PMCID: PMC11546680
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111159
Impacts of low birthweight on kidney development and intergenerational growth of the offspring
Abstract
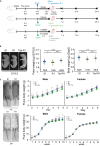
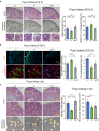
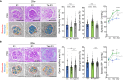
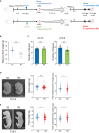
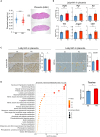
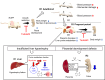
Low birthweight (LBW) increases the risk of adult-onset diseases, including kidney diseases, with intergenerational consequences; however, the underlying mechanisms and effective interventions are unclear. To examine the cross-generational effects of LBW, we established an LBW mouse model through reduced uterine perfusion pressure (RUPP) and investigated the therapeutic potential of tadalafil, a phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor, on LBW-associated consequences. RUPP-pups (R1) had lower fetal and birth weights, delayed renal development, and fewer glomeruli than Sham-pups. In adulthood, R1 mice exhibited persistently fewer glomeruli and elevated blood pressure, while Tadalafil-R1 mice showed reduced hypertension in both sexes and improved renal pathological changes in males. Additionally, pregnant R1 mice displayed inadequate gestational liver hypertrophy, impaired hepatic purine metabolism, and diminished placental angiogenesis, resulting in fetal growth restriction in the subsequent generation. These findings underscore the lasting impact of LBW on adult health and future generations and suggest tadalafil's potential to mitigate LBW-associated risks.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Metabolomics; Physiology.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . 2022. International classification of diseases, eleventh revision ICD-11. Relatório técnico.
-
- Okwaraji Y.B., Krasevec J., Bradley E., Conkle J., Stevens G.A., Gatica-Domínguez G., Ohuma E.O., Coffey C., Estevez Fernandez D.G., Blencowe H., et al. National, regional, and global estimates of low birthweight in 2020, with trends from 2000: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2024;403:1071–1080. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01198-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- White S.L., Perkovic V., Cass A., Chang C.L., Poulter N.R., Spector T., Haysom L., Craig J.C., Salmi I.A., Chadban S.J., Huxley R.R. Is low birth weight an antecedent of CKD in later life? A systematic review of observational studies. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009;54:248–261. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.12.042. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

