Spectral Graph Sample Weighting for Interpretable Sub-cohort Analysis in Predictive Models for Neuroimaging
- PMID: 39525051
- PMCID: PMC11549025
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-74561-4_3
Spectral Graph Sample Weighting for Interpretable Sub-cohort Analysis in Predictive Models for Neuroimaging
Abstract
Recent advancements in medicine have confirmed that brain disorders often comprise multiple subtypes of mechanisms, developmental trajectories, or severity levels. Such heterogeneity is often associated with demographic aspects (e.g., sex) or disease-related contributors (e.g., genetics). Thus, the predictive power of machine learning models used for symptom prediction varies across subjects based on such factors. To model this heterogeneity, one can assign each training sample a factor-dependent weight, which modulates the subject's contribution to the overall objective loss function. To this end, we propose to model the subject weights as a linear combination of the eigenbases of a spectral population graph that captures the similarity of factors across subjects. In doing so, the learned weights smoothly vary across the graph, highlighting sub-cohorts with high and low predictability. Our proposed sample weighting scheme is evaluated on two tasks. First, we predict initiation of heavy alcohol drinking in young adulthood from imaging and neuropsychological measures from the National Consortium on Alcohol and NeuroDevelopment in Adolescence (NCANDA). Next, we detect Dementia vs. Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) using imaging and demographic measurements in subjects from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI). Compared to existing sample weighting schemes, our sample weights improve interpretability and highlight sub-cohorts with distinct characteristics and varying model accuracy.
Figures
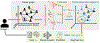

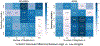
References
-
- Cho K, et al. : Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1406.1078 (2014)
-
- Chung F: Spectral Graph Theory. American Mathematical Society, Providence, R.I (1997)
Grants and funding
- R37 AA010723/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AA021697/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA021696/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA021691/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA021695/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA021692/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AA028840/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AA028840/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AA021695/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA021690/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA057567/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA021697/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA010723/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
