A clenbuterol detection method based on magnetic separation up-conversion fluorescent probe
- PMID: 39525055
- PMCID: PMC11547955
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101911
A clenbuterol detection method based on magnetic separation up-conversion fluorescent probe
Abstract
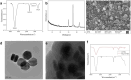
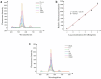
In this study, a fluorescence detection method combining aptamer-modified up-conversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) and magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) was developed for detection of Clenbuterol (CLB). The aptamer-modified magnetic NPs captured CLB, which reacted with the aptamer-modified UCNPs and generated a sandwich complex. The aptamer-modified UCNPs acted as a fluorescence source. The MNP-CLB-UCNP complex was retrieved from the solution using an magnetic field, and the fluorescence intensity was detected by fluorescence spectrophotometry with excitation and emission spectra at 980 nm and in the 400-800 nm region, respectively. The results showed that the fluorescence intensity gradually increased with increasing concentrations of CLB with a good specify. The method was highly sensitive for the quantification of CLB, with a limit of detection of 0.304 ng mL-1. The recovery rate of CLB from pork samples ranged from 84 % to 94.87 %. This fluorescence method enables the sensitive, precise, and accurate quantification of CLB residues in pork samples.
Keywords: Aptamer; Clenbuterol; Detection method; Magnetic nanoparticles; Up-conversion nanoparticles.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A dual-responsive fluorescence method for the detection of clenbuterol based on BSA-protected gold nanoclusters.Anal Chim Acta. 2015 Apr 29;871:43-50. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2015.02.031. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Anal Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 25847160
-
Visualization and colorimetric determination of clenbuterol in pork by using magnetic beads modified with aptamer and complementary DNA as capture probes, and G-quadruplex/hemin and DNA antibody on the metal-organic framework MIL-101(Fe) acting as a peroxidase mimic.Mikrochim Acta. 2019 Jul 6;186(8):515. doi: 10.1007/s00604-019-3604-5. Mikrochim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31280384
-
A Nanosensor Based on Carbon Dots for Recovered Fluorescence Detection Clenbuterol in Pork Samples.J Fluoresc. 2017 Sep;27(5):1847-1853. doi: 10.1007/s10895-017-2122-2. Epub 2017 Jun 20. J Fluoresc. 2017. PMID: 28634884
-
Fluorescence immunoassay for simultaneous detection typical β-agonists in animal derived food using blue-green upconversion nanoparticles as labels.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2023 Dec 15;303:123253. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2023.123253. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2023. PMID: 37579663
-
Rapid and selective detection of Bacillus cereus in food using cDNA-based up-conversion fluorescence spectrum copy and aptamer modified magnetic separation.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2022 Feb 15;267(Pt 2):120618. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.120618. Epub 2021 Nov 13. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2022. PMID: 34802926
Cited by
-
Recent Progress on Rare-Earth-Doped Upconversion Nanomaterials for Bioassay Applications.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 May 23;15(6):335. doi: 10.3390/bios15060335. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40558417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allegrini F., Olivieri A., C. IUPAC-consistent approach to the limit of detection in partial least-squares calibration. Analytical Chemistry. 2014;86(15):7858–7866. - PubMed
-
- Bayat P., Nosrati R., Alibolandi M., Rafatpanah H., Abnous K., Khedri M., Ramezani M. SELEX methods on the road to protein targeting with nucleic acid aptamers. Biochimie. 2018;154:132–155. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

