Electrostatically-enhanced two-stage low-temperature tempering: Effects on the quality of frozen tan mutton
- PMID: 39525067
- PMCID: PMC11550020
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101926
Electrostatically-enhanced two-stage low-temperature tempering: Effects on the quality of frozen tan mutton
Abstract
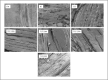
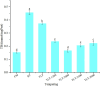
The two-stage low-temperature tempering (TLT) and TLT assisted by electrostatic fields (TLT-1500/2000/2500/3000) were developed to investigate their effects on the quality of frozen Tan mutton. The results demonstrated that both TLT and TLT-1500/2000/2500/3000 significantly (P < 0.05) enhanced the tempering rate compared to refrigerator tempering (4 °C, RT). The analysis of tempering, cooking, and centrifugal losses, along with the evaluation of electrical conductivity, pH, and TVB-N, showed that the water retention capacity and freshness of Tan mutton treated with TLT-2500 were closest to those of fresh Tan mutton. Scanning electron microscopy analysis demonstrated that TLT-2500 best maintained the tissue integrity of Tan mutton, while low-field nuclear magnetic resonance analysis revealed it contained the highest immobile water and least free water. Furthermore, Tan mutton treated with TLT-2000 and TLT-2500 exhibited minimal lipid oxidation and color change. In contrast, the most significant changes in all indicators were observed after RT.
Keywords: Electrostatic field assistance; Tan mutton; Tempering methods; Two-stage low-temperature tempering.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Amiri A., Mousakhani-Ganjeh A., Shafiekhani S., Mandal R., Singh A.P., Kenari R.E. Effect of high voltage electrostatic field thawing on the functional and physicochemical properties of myofibrillar proteins. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies. 2019;56 doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2019.102191. - DOI
-
- Bekhit A.E.-D.A., Holman B.W.B., Giteru S.G., Hopkins D.L. Total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) and its role in meat spoilage: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2021;109:280–302. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.01.006. - DOI
-
- Cao M., Cao A., Wang J., Cai L., Regenstein J., Ruan Y., Li X. Effect of magnetic nanoparticles plus microwave or far-infrared thawing on protein conformation changes and moisture migration of red seabream (Pagrus Major) fillets. Food Chemistry. 2018;266:498–507. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.057. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

