Sodium and Hematocrit Levels' Correlation and Clinical Impacts in Jordanian Hemodialysis Patients
- PMID: 39525164
- PMCID: PMC11550108
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.71208
Sodium and Hematocrit Levels' Correlation and Clinical Impacts in Jordanian Hemodialysis Patients
Abstract
Aim: Given cofounders, this retrospective study investigates the correlation between hyponatremia status and hematocrit (Hct) changes, as well as the clinical utility of these two prognosticators in relation to overall health status.
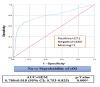
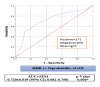
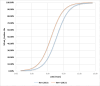
Methods: The study was retrospectively conducted on adult hemodialysis (HD) patients at the King Hussein Medical Center in Amman, Jordan, from 2015 to 2022. It looked at how sodium (Na) levels, the hematocrit-to-hemoglobin ratio (HHR), and outcomes of interest were related. The study examined acute myocardial infarction, stroke, refractory hypertension, dialysis graft thrombosis, and all-cause mortality as the composite outcomes of interest (cOI). We conducted a series of receiver operating characteristics, binary logistic regression (BLgR), and sensitivity analyses between each tested prognosticator and the cOI. We constructed and illustrated a multiple logistic regression (MLgR) model to investigate the adjusted association of each prognosticator against the tested composite outcome probability.
Results: The majority of HD patients were hemolyzed for a period of four to seven years. The constructed binary regression modeling for each prognosticator was [e (109.36 - 0.849 × Na)/[1 + e (109.36 - 0.849 × Na)] and [e (16.033 - 6.388 × HHR)/[1 + e (16.033 - 6.388 ×HHR)], with a 35.57% probability of cOI at the optimal Na of 129.51 mEq/l and a 42.8% at optimal HHR of 2.555:1. When the length of hemodialysis (LOD) was introduced into the MLgR modeling all the investigated independent variables were significant except the HHR (p-value = 0.908).
Conclusion: A higher LOD, lower Na, and lower HHR all support a positive cOI probability status. Regular inspection of Na and HHR and ensuring their closet to their optimal thresholds are mandatory to mitigate the risk of higher cOI probability.
Keywords: health care outcomes; hematocrit to hemoglobin ratio; hyponatraemia; intermittent hemodialysis (ihd); jordanian; optimal threshold.
Copyright © 2024, Al Hindawi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Jordanian Institutional Review Board of Royal Medical Services issued approval 17_10/2023. The Jordanian Royal Medical Services committee approved this manuscript for publication on November 13, 2023. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures




References
-
- Correlation between the laboratory features-thrombocytopenia, elevated hepatic enzymes, hyponatremia, high hematocrit and severity of dengue infection. Sundaramurthy N. https://healthcare-bulletin.co.uk/article/volume-13-issue-1-pages273-278... Eur J Cardiovasc Med . 2023;13:273–278.
-
- Comparison of blood gas analysis parameters, biochemical tests and hematological parameters in geriatric patients admitted to the emergency department. Bilge A, Akça HŞ, Özkan A. J Clin Med Kaz. 2023 ;20:60–64.
-
- Challenge in hyponatremic patients-the potential of a laboratory-based decision support system for hyponatremia to improve patient's safety. Sicker T, Federbusch M, Eckelt F, et al. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2023;61:1025–1034. - PubMed
-
- Response to salinity challenge in non-native Cichlid fishes of the genus Herichthys introduced in the Gulf Coast Region of the United States. Oldfield RG, Hooks J, Sommer J, et al. Ichthyol Herpetol. 2021;109:587–597.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
