Augmented glycerosomes as a promising approach against fungal ear infection: Optimization and microbiological, ex vivo and in vivo assessments
- PMID: 39525529
- PMCID: PMC11543555
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2024.100295
Augmented glycerosomes as a promising approach against fungal ear infection: Optimization and microbiological, ex vivo and in vivo assessments
Abstract
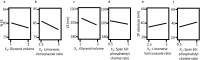
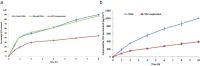
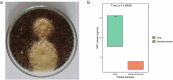
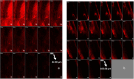
In the current study, voriconazole (VCZ) augmented glycerosomes were optimized for topical otomycosis management according to a 23 factorial design, employing a thin film hydration method. By optimizing Glycerol volume, limonene: VCZ ratio and Span® 60: soybean phosphatidyl choline (PC) ratio, glycerosomes with maximum percentage entrapment efficiency (%EE) and zeta potential (ZP) and minimum vesicle size (VS) and polydispersity index (PDI) were to be obtained. An optimal augmented glycerosomal formula (OAG) that contained 10 mg VCZ, 150 mg PC, and 3 mL glycerol, comprising 2.5: and 0.92:1 ratios of the latter two independent variables, was proposed via numerical optimization. OAG exhibited high %EE and ZP values and acceptable low values for VS and PDI (84.3 ± 2.0 %, -38.8 ± 1.8 mV, 191.0 ± 1.1 nm, and 0.192 ± 0.01, respectively). Extensive in vitro testing of OAG revealed the entrapment of VCZ within OAG, biphasic in vitro release profile, stability for up to 3 months at 2-8 °C and spherical morphology of OAG with VS like that obtained via zetasizer. OAG demonstrated higher permeated amounts of VCZ and flux values than VCZ suspension, leading to an enhancement ratio of 2.56 in the ex vivo permeation study. The deeper penetration ability of OAG demonstrated by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy and its superior in vitro antifungal activity confirmed the validity of the ex vivo study. Also, the histopathological study confirmed the safety of OAG for topical use, suggesting that VCZ OAG was a promising topical antimycotic formula.
Keywords: Augmented glycerosomes; Factorial design; Minimal fungicidal concentration; Otomycosis; Transmission electron microscopy; Voriconazole.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Statistical optimization of hyaluronic acid enriched ultradeformable elastosomes for ocular delivery of voriconazole via Box-Behnken design: in vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation.Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):77-86. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1858997. Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 33342315 Free PMC article.
-
Crisaborole-Enthused Glycerosomal Gel for an Augmented Skin Permeation.Recent Adv Drug Deliv Formul. 2024;18(2):120-130. doi: 10.2174/0126673878283299240418112318. Recent Adv Drug Deliv Formul. 2024. PMID: 38659269
-
Bilosomes as Promising Nanovesicular Carriers for Improved Transdermal Delivery: Construction, in vitro Optimization, ex vivo Permeation and in vivo Evaluation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Dec 8;15:9783-9798. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S278688. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33324052 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and optimization of fisetin loaded glycerol based soft nanovesicles by Box-Behnken design.Int J Pharm. 2020 Mar 30;578:119125. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119125. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32036010
-
A comprehensive review on recent nanosystems for enhancing antifungal activity of fenticonazole nitrate from different routes of administration.Drug Deliv. 2023 Dec;30(1):2179129. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2023.2179129. Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 36788709 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Terconazole loaded edge-activated hybrid elastosome for revamped corneal permeation in ocular mycosis: In-vitro characterization, statistical optimization, microbiological assessment, and in-vivo evaluation.Int J Pharm X. 2025 Apr 8;9:100333. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2025.100333. eCollection 2025 Jun. Int J Pharm X. 2025. PMID: 40292341 Free PMC article.
-
Electrospun Nanofiber-Scaffold-Loaded Levocetirizine Dihydrochloride Cerosomes for Combined Management of Atopic Dermatitis and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) Skin Infection: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Apr 27;18(5):633. doi: 10.3390/ph18050633. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430454 Free PMC article.
-
Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems: Methods for Enhancing Skin Permeability and Their Evaluation.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 20;17(7):936. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070936. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40733144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and characterization of fenticonazole nitrate-loaded cubogel for the management of vaginal candidiasis.Int J Pharm X. 2025 Jul 10;10:100355. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2025.100355. eCollection 2025 Dec. Int J Pharm X. 2025. PMID: 40703664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdelbary A.A., AbouGhaly M.H. Design and optimization of topical methotrexate loaded niosomes for enhanced management of psoriasis: application of Box–Behnken design, in-vitro evaluation and in-vivo skin deposition study. Int. J. Pharm. 2015;485:235–243. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.03.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abdelbary A.A., Abd-Elsalam W.H., Al-Mahallawi A.M. Fabrication of novel ultradeformable bilosomes for enhanced ocular delivery of terconazole: in vitro characterization, ex vivo permeation and in vivo safety assessment. Int. J. Pharm. 2016;513:688–696. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.10.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abdelrahman F.E., Elsayed I., Gad M.K., Elshafeey A.H., Mohamed M.I. Response surface optimization, ex vivo and in vivo investigation of nasal spanlastics for bioavailability enhancement and brain targeting of risperidone. Int. J. Pharm. 2017;530:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.07.050. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

