Dopamine internalization via Uptake2 and stimulation of intracellular D5-receptor-dependent calcium mobilization and CDP-diacylglycerol signaling
- PMID: 39525629
- PMCID: PMC11543475
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1422998
Dopamine internalization via Uptake2 and stimulation of intracellular D5-receptor-dependent calcium mobilization and CDP-diacylglycerol signaling
Abstract
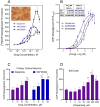
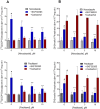
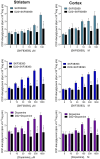
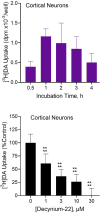
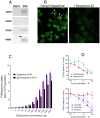
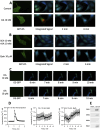
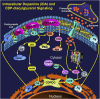
Dopamine stimulates CDP-diacylglycerol biosynthesis through D1-like receptors, particularly the D5 subtype most of which is intracellularly localized. CDP-diacylglycerol regulates phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate-dependent signaling cascades by serving as obligatory substrate for phosphatidylinositol biosynthesis. Here, we used acute and organotypic brain tissues and cultured cells to explore the mechanism by which extracellular dopamine acts to modulate intracellular CDP-diacylglycerol. Dopamine stimulated CDP-diacylglycerol in organotypic and neural cells lacking the presynaptic dopamine transporter, and this action was selectively mimicked by D1-like receptor agonists SKF38393 and SKF83959. Dopaminergic CDP-diacylglycerol stimulation was blocked by decynium-22 which blocks Uptake2-like transporters and by anti-microtubule disrupters of cytoskeletal transport, suggesting transmembrane uptake and guided transport of the ligands to intracellular sites of CDP-diacylglycerol regulation. Fluorescent or radiolabeled dopamine was saturably transported into primary neurons or B35 neuroblastoma cells expressing the plasmamembrane monoamine transporter, PMAT. Microinjection of 10-nM final concentration of dopamine into human D5-receptor-transfected U2-OS cells rapidly and transiently increased cytosolic calcium concentrations by 316%, whereas non-D5-receptor-expressing U2-OS cells showed no response. Given that U2-OS cells natively express PMAT, bath application of 10 μM dopamine slowly increased cytosolic calcium in D5-expressing cells. These observations indicate that dopamine is actively transported by a PMAT-implicated Uptake2-like mechanism into postsynaptic-type dopaminoceptive cells where the monoamine stimulates its intracellular D5-type receptors to mobilize cytosolic calcium and promote CDP-diacylglycerol biosynthesis. This is probably the first demonstration of functional intracellular dopamine receptor coupling in neural tissue, thus challenging the conventional paradigm that postsynaptic dopamine uptake serves merely as a mechanism for deactivating spent or excessive synaptic transmitter.
Keywords: CDP-diacylglycerol; D5 dopamine receptor; calcium mobilization; dopamine uptake; nucleolipid; phosphatidylinositol; plasmamembrane monoamine transporter; uptake2.
Copyright © 2024 Kang, Siewe, Oluigbo, Arijesudade, Brailoiu and Undieh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antidepressant stimulation of CDP-diacylglycerol synthesis does not require monoamine reuptake inhibition.BMC Neurosci. 2010 Jan 27;11:10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-11-10. BMC Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20105322 Free PMC article.
-
D1/D5 dopamine receptors stimulate intracellular calcium release in primary cultures of neocortical and hippocampal neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2002 Apr;87(4):2167-75. doi: 10.1152/jn.00541.2001. J Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 11929934
-
Dopamine induces release of calcium from internal stores in layer II lateral entorhinal cortex fan cells.Cell Calcium. 2019 Jun;80:103-111. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2019.04.003. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Cell Calcium. 2019. PMID: 30999216
-
Coupling of D1 and D5 dopamine receptors to multiple G proteins: Implications for understanding the diversity in receptor-G protein coupling.Mol Neurobiol. 1998 Apr;16(2):125-34. doi: 10.1007/BF02740640. Mol Neurobiol. 1998. PMID: 9588624 Review.
-
The peripheral dopaminergic system: morphological analysis, functional and clinical applications.Ital J Anat Embryol. 2002 Jul-Sep;107(3):145-67. Ital J Anat Embryol. 2002. PMID: 12437142 Review.
References
-
- Baufreton J., Garret M., Rivera A., de la C. A., Gonon F., Dufy B., et al. (2003). D5 (not D1) dopamine receptors potentiate burst-firing in neurons of the subthalamic nucleus by modulating an L-type calcium conductance. J. Neurosci. 23 (3), 816–825. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-03-00816.2003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

