Setmelanotide: A Melanocortin-4 Receptor Agonist for the Treatment of Severe Obesity Due to Hypothalamic Dysfunction
- PMID: 39526054
- PMCID: PMC11548362
- DOI: 10.17925/EE.2024.20.2.9
Setmelanotide: A Melanocortin-4 Receptor Agonist for the Treatment of Severe Obesity Due to Hypothalamic Dysfunction
Abstract
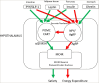
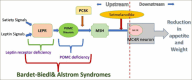
Obesity is a silent global pandemic. It is a condition associated with multiple risk factors and adverse outcomes that arise from the intertwined relationship between environmental factors and genetics. The genetic factors that cause phenotypic expression are variable. Monogenic obesity is a severe early-onset and rarer form of obesity, which presents with co-morbidities such as abnormal feeding behaviour. Monogenic obesity causes impaired weight regulation in the hypothalamus due to defects in the leptin-melanocortin signalling pathway. The emergence of a new therapeutic treatment, the melanocortin-4 receptor agonist setmelanotide (originally RM-493), has represented a breakthrough in the management of monogenic obesity and has raised hope in managing complex obesity. This review provides an overview of the setmelanotide trials that have taken place, as well as its mechanism of action, side effects and weight loss outcomes that led to its approval in the treatment of pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) deficiency and proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 (PCSK1) deficiency. It also explores setmelanotide's role in other genetic forms of obesity, such as hypothalamic obesity, Prader-Willi syndrome, Alström syndrome and other rare genetic conditions that are being investigated. This review aims to help to understand the pathophysiology of genetic obesity and aid in future treatment options for people with severe, complex genetic obesity.
Keywords: Hypothalamic dysfunction; leptin–melanocortin signalling pathway; melanocortin-4 receptor agonist; monogenic obesity; setmelanotide; syndromic obesity.
© Touch Medical Media 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: Sulmaaz Qamar has received Funding from the National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) UCLH Biomedical Research Centre. Ritwika Mallik has received Funding from the National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) UCLH Biomedical Research Centre. Janine Makaronidis has received Funding from the National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) UCLH Biomedical Research Centre and the Society for Endocrinology. Institutional funding from NovoNordisk, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals and Innovate UK.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. 2021. www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight Available at: (Date last accessed: 11 March 2023)
-
- World Obesity Atlas. World Obesity Federation. 2022. www.worldobesity.org/resources/resource-library/world-obesity-atlas-2022 Available at: (Date last accessed: 31 May 2023)
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous