Intravenous thrombolysis plus tirofiban versus tirofiban alone in Caucasian patients with acute anterior choroidal or paramedian pontine infarction
- PMID: 39526109
- PMCID: PMC11542752
- DOI: 10.4103/bc.bc_15_24
Intravenous thrombolysis plus tirofiban versus tirofiban alone in Caucasian patients with acute anterior choroidal or paramedian pontine infarction
Abstract
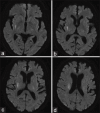
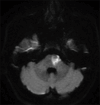
Background: Tirofiban has been shown to be superior to aspirin in achieving functional independence at 3 months for acute ischemic stroke of atheromatous or microatheromatous origin. As intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) has previously been shown to be nonsuperior to aspirin in achieving functional independence at 3 months for anterior choroidal or paramedian pontine infarction (ACI/PPI), we aimed to compare the outcomes of Caucasian patients receiving IVT plus tirofiban (IVT + T) with those receiving tirofiban alone for acute ACI/PPI.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted in patients aged ≥ 18 years with ACI/PPI treated in our stroke unit between December 1, 2020, and April 30, 2023, who received therapeutic intervention within 9 hours of symptom onset or after awakening with stroke symptoms. Modified Rankin Scale (mRS) ≤ 1 at 3 months was the primary endpoint. Secondary endpoints were National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) ≤ 2 at day 7 or discharge and post-procedural neurological deterioration (PPND) within 72 hours. Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (SICH) and major systemic bleeding (MSB) were the safety measures of the study.
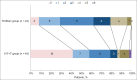
Results: A total of 24 patients were enrolled in the tirofiban group and 43 patients in the IVT + T group. Compared to tirofiban alone, IVT + T was associated with a higher probability of achieving mRS ≤1 at 3 months (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 8.79; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.06-37.52; P = 0.003) and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale ≤2 at day 7 or discharge (aOR, 3.70; 95% CI, 1.05-12.99; P = 0.041). No significant difference was seen between the two groups in preventing postprocedural neurological deterioration. One case of SICH and two cases of MSB occurred in the IVT + T group and no cases in the tirofiban group. One case of inhospital mortality was recorded in the IVT + T group.
Conclusions: Our results showed that IVT + T may be safe and effective in Caucasian patients with acute ACI/PPI.
Keywords: Acute ischemic stroke; anterior choroidal artery; intravenous thrombolysis; paramedian pontine artery; tirofiban.
Copyright: © 2024 Brain Circulation.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke:2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50:e344–418. - PubMed
-
- Chausson N, Joux J, Saint-Vil M, Edimonana M, Jeannin S, Aveillan M, et al. Infarction in the anterior choroidal artery territory: Clinical progression and prognosis factors. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014;23:2012–7. - PubMed
-
- Cheng Z, Duan H, Meng F, Du H, Zhang W, Li H, et al. Acute anterior choroidal artery territory infarction: A retrospective study. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020;195:105826. - PubMed
-
- Park MG, Oh EH, Kim BK, Park KP. Intravenous tissue plasminogen activator in acute branch atheromatous disease: Does it prevent early neurological deterioration? J Clin Neurosci. 2016;33:194–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
