In vitro regeneration and Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Caragana korshinskii
- PMID: 39526255
- PMCID: PMC11524263
- DOI: 10.48130/FR-2023-0014
In vitro regeneration and Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Caragana korshinskii
Abstract
Caragana korshinskii is a deciduous shrub with large eco-economic value and strong tolerance to abiotic stresses. However, the shortage of reliable genetic transformation technology severely hinders its research on stress tolerance mechanisms and stress-resistant gene mining and application. In this study, the embryonic tip of the C. korshinskii seedling was used as the initiating explant to get regenerated plant through the direct organogenesis pathway, which significantly shortened the culture cycle and set the foundation for investigation of Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation. Our results suggest that the embryonic tip possesses robust meristem capacity and is an efficient method for transgenic breeding. This research provides a technical basis for asexual reproduction, molecular breeding, and gene function investigation in C. korshinskii by establishing, for the first time, an effective in vitro regeneration system and an Agrobacterium-mediated stable genetic transformation system utilizing the embryonic tip of C. korshinskii as explants.
Keywords: Agrobacterium-mediated transformation; Embryonic tip; Caragana korshinskii; Organogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
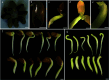



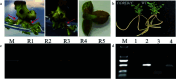
Similar articles
-
Effects of drought and salt-stresses on gene expression in Caragana korshinskii seedlings revealed by RNA-seq.BMC Genomics. 2016 Mar 8;17:200. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2562-0. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26951633 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of drought response genes by digital gene expression (DGE) analysis in Caragana korshinskii Kom.Gene. 2020 Jan 30;725:144170. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144170. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Gene. 2020. PMID: 31647996
-
Genomic insights into drought adaptation of the forage shrub Caragana korshinskii (Fabaceae) widely planted in drylands.Plant J. 2025 Feb;121(3):e17255. doi: 10.1111/tpj.17255. Plant J. 2025. PMID: 39912348
-
Mechanistic insights derived from re-establishment of desiccation tolerance in germinating xerophytic seeds: Caragana korshinskii as an example.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Nov 7;13:1029997. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1029997. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36420023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improvement of tissue culture, genetic transformation, and applications of biotechnology to Brassica.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2017 Apr;33(1):1-25. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2017.1309821. Epub 2017 May 2. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2017. PMID: 28460558 Review.
Cited by
-
Somatic Embryogenesis and Genetic Transformation of Caragana intermedia.Plants (Basel). 2025 May 21;14(10):1545. doi: 10.3390/plants14101545. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40431111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Z, Gao H Progress on genetic diversity of genus Caragana germplasm resources. Journal of Plant Genetic Resource. 2008;9:397–400.
-
- Zhao Y Taxonomic studies on the genus Caragana from China. Journal of Inner Mongolia Uniwersity. 1993;24:631–53.
-
- Niu X Suggestions on vigorously develop Caragana forest in northwest China. Inner Mongolian Animal Husbandry Sciences. 1999;1999(1):20–24.
-
- LI J, Xie L, Ren J, Gong C Functional analysis of CkPHB gene regulation xylem development and enhancing plant drought resistance in Caragana korshinskii. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalla Sinica. 2021;41:1259–66.
-
- Guan JL, Ma CC The research progress of Caragana species during the 21st century. Acta AgrestiaSinica. 2014;22:697–705.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
