Overexpression of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase enhances the monoterpene content in Litsea cubeba
- PMID: 39526280
- PMCID: PMC11524321
- DOI: 10.48130/FR-2023-0011
Overexpression of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase enhances the monoterpene content in Litsea cubeba
Abstract
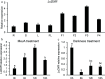
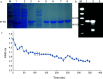
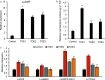
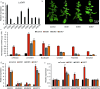
Monoterpenes are important components of plant essential oils and have long been used as raw materials for spices and food flavorings. Litsea cubeba is an economically aromatic plant species, the fruits of which produce essential oil with monoterpenes as the dominant components. As a branch point of carbon flow in the methyl erythritol phosphate (MEP) biosynthesis pathway, 1-deoxy-D-xylo-5-phosphate reductoisomerase (DXR) is a key rate-limiting enzyme that catalyzes the MEP pathway's second committed step. Therefore, DXR has become an effective regulation target to improve the biosynthesis of plant monoterpenes. In this study, we identified a DXR from L. cubeba, which was highly expressed in fruits, induced by MeJA and repressed by darkness. An enzyme assay showed that recombination LcDXR protein catalyzed DXP with NADPH as the cofactor. Transient overexpression of LcDXR significantly increased the content of monoterpenes in L. cubeba. Furthermore, LcDXR-overexpressing tobaccos were conducted and showed almost 5.9-fold increase in monoterpenes production, including limonene, α-pinene, eucalyptol, linalool, terpineol and camphor. Overexpression of LcDXR activated the metabolic flux of monoterpene biosynthesis through crosstalk and feedback mechanism. In addition, LcDXR-overexpressing tobaccos had no effect on phenotype of transgenic tobaccos. Our results demonstrate that LcDXR is a critical regulator of the monoterpene production in L. cubeba and other plants.
Keywords: DXP reductoisomerase; Litsea cubeba; MEP pathway; Monoterpene.
Conflict of interest statement
Yicun Chen is the Editorial Board member of Forestry Research. She was blinded from reviewing or making decisions on the manuscript. The article was subject to the journal's standard procedures, with peer-review handled independently of this Editorial Board member and her research groups.
Figures

Similar articles
-
LcMYB106 suppresses monoterpene biosynthesis by negatively regulating LcTPS32 expression in Litsea cubeba.Tree Physiol. 2023 Dec 12;43(12):2150-2161. doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpad111. Tree Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37682081
-
Deoxyxylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase is not a rate-determining enzyme for essential oil production in spike lavender.J Plant Physiol. 2014 Nov 1;171(17):1564-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2014.07.012. Epub 2014 Aug 1. J Plant Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25151124
-
LcMYB43 enhances monoterpene biosynthesis by activating 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase gene expression in Litsea cubeba.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Apr;304(Pt 1):140860. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140860. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39938834
-
Targeting the methyl erythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway for novel antimalarial, antibacterial and herbicidal drug discovery: inhibition of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase (DXR) enzyme.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(11):1161-77. doi: 10.2174/138161207780618939. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17430177 Review.
-
Mechanism and inhibition of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase.Bioorg Chem. 2014 Dec;57:171-185. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2014.06.001. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Bioorg Chem. 2014. PMID: 24998420 Review.
Cited by
-
Biosynthetic Machinery to Abiotic Stress-Driven Emission: Decoding Multilayer Regulation of Volatile Terpenoids in Plants.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 May 31;14(6):673. doi: 10.3390/antiox14060673. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive characterization of volatile terpenoids and terpene synthases in Lanxangia tsaoko.Mol Hortic. 2025 Apr 3;5(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s43897-024-00140-0. Mol Hortic. 2025. PMID: 40176169 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Analysis of Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Reveals Key Genes Involved in Terpenes Biosynthesis Pathway of Litsea cubeba Under Light and Darkness Treatments.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 25;26(7):2992. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072992. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243633 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
