DRAMP 4.0: an open-access data repository dedicated to the clinical translation of antimicrobial peptides
- PMID: 39526377
- PMCID: PMC11701585
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1046
DRAMP 4.0: an open-access data repository dedicated to the clinical translation of antimicrobial peptides
Abstract
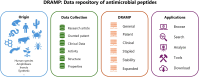
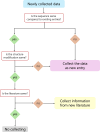
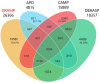
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are potential candidates for treating multidrug-resistant bacterial infections, yet only a small number of them have progressed into clinical trials. The main challenges include the poor stability and hemolytic/cytotoxic properties of AMPs. Considering this, in the update of the Data Repository of Antimicrobial Peptides (DRAMP), a new annotation on serum and protease stability is added, and special efforts were made to update the hemolytic/cytotoxic information of AMPs. The DRAMP 4.0 currently holds 30 260 entries (8 001 newly added), consisting of 11 612 general entries, 17 886 patent entries, 96 clinical entries, 377 specific entries, 110 entries with stability data, and 179 expanded entries. A total of 2891 entries possess experimentally determined hemolytic activity information, while 2674 entries contain cytotoxicity data by experimental validation. The update also covers new annotations, statistics, categories, functions, and download links. DRAMP is available online at http://dramp.cpu-bioinfor.org/.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial peptide biological activity, delivery systems and clinical translation status and challenges.J Transl Med. 2025 Mar 7;23(1):292. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06321-9. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40055730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DRAMP 3.0: an enhanced comprehensive data repository of antimicrobial peptides.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jan 7;50(D1):D488-D496. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab651. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 34390348 Free PMC article.
-
DRAMP 2.0, an updated data repository of antimicrobial peptides.Sci Data. 2019 Aug 13;6(1):148. doi: 10.1038/s41597-019-0154-y. Sci Data. 2019. PMID: 31409791 Free PMC article.
-
DRAMP: a comprehensive data repository of antimicrobial peptides.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 14;6:24482. doi: 10.1038/srep24482. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27075512 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in peptide-based antimicrobials: A possible option for emerging drug-resistant infections.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2024 Nov;333:103282. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2024.103282. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2024. PMID: 39276418 Review.
Cited by
-
AVPpred-BWR: antiviral peptides prediction via biological words representation.Bioinformatics. 2025 Mar 29;41(4):btaf126. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf126. Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40152250 Free PMC article.
-
ToxiPep: Peptide toxicity prediction via fusion of context-aware representation and atomic-level graph.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025 May 28;27:2347-2358. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.05.039. eCollection 2025. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 40529180 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Generative Models for the Discovery of Antiviral Peptides Targeting Dengue Virus: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 26;26(13):6159. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136159. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive dataset of therapeutic peptides on multi-function property and structure information.Sci Data. 2025 Jul 14;12(1):1213. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-05528-1. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40659670 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial peptide biological activity, delivery systems and clinical translation status and challenges.J Transl Med. 2025 Mar 7;23(1):292. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06321-9. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40055730 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xuan J., Feng W., Wang J., Wang R., Zhang B., Bo L., Chen Z.-S., Yang H., Sun L.. Antimicrobial peptides for combating drug-resistant bacterial infections. Drug Resist. Updat. 2023; 68:100954. - PubMed
-
- Bucataru C., Ciobanasu C.. Antimicrobial peptides: opportunities and challenges in overcoming resistance. Microbiol. Res. 2024; 286:127822. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

