Targeting CLK2 and serine/arginine-rich splicing factors inhibits multiple myeloma through downregulating RAE1 by nonsense-mediated mRNA decay mechanism
- PMID: 39526400
- PMCID: PMC11711041
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.16387
Targeting CLK2 and serine/arginine-rich splicing factors inhibits multiple myeloma through downregulating RAE1 by nonsense-mediated mRNA decay mechanism
Abstract
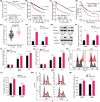
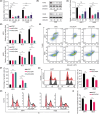
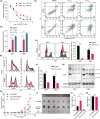
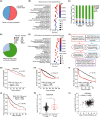
Multiple myeloma (MM) is closely related to abnormal RNA splicing in its pathogenesis. CDC2-like kinase-2 (CLK2) regulates RNA splicing by phosphorylating serine/arginine-rich splicing factors (SRSFs), but the role of CLK2 in MM remains undefined. This study was to explore the role and mechanism of CLK2 in MM. Analyzing GEO datasets of MM patients found that high CLK2 expression predicted poor prognosis. Overexpression of CLK2 promoted the cell proliferation and cell cycle progression of MM cell ARP1 and H929. Knockdown or inhibition of CLK2 suppressed cell proliferation and induced cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in ARP1 and H929 cells in vitro. An MM xenograft tumor experiment showed that CLK2 overexpression promoted tumor growth, while CLK2 inhibition suppressed tumor growth in vivo. Mechanistic studies revealed that interfering CLK2 inhibited SRSF phosphorylation, and induced exon 9 skipping of RAE1, resulting in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) of RAE1. In addition, RAE1 knockdown inhibited cell proliferation in ARP1 and H929 cells. Moreover, RAE1 overexpression promoted cell proliferation and cell cycle progression of ARP1 and H929 cells, and partially reversed the antitumor effect of CLK2 knockdown. Targeting CLK2 shows antitumor effects on MM partially through inhibiting SRSF phosphorylation and inducing NMD of RAE1. Therefore, targeting the CLK2/SRSFs/RAE1 axis could be a potential therapeutic strategy for MM.
Keywords: CLK2; RAE1; SRSF; alternative splicing; nonsense‐mediated mRNA decay.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest for this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting the CLK2/SRSF9 splicing axis in prostate cancer leads to decreased ARV7 expression.Mol Oncol. 2025 Feb;19(2):496-518. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13728. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Mol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39258426 Free PMC article.
-
The CLK inhibitor SM08502 induces anti-tumor activity and reduces Wnt pathway gene expression in gastrointestinal cancer models.Cancer Lett. 2020 Mar 31;473:186-197. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2019.09.009. Epub 2019 Sep 24. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 31560935
-
CLK1/SRSF5 pathway induces aberrant exon skipping of METTL14 and Cyclin L2 and promotes growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Apr 13;14(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01072-8. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33849617 Free PMC article.
-
A critical update on the strategies towards small molecule inhibitors targeting Serine/arginine-rich (SR) proteins and Serine/arginine-rich proteins related kinases in alternative splicing.Bioorg Med Chem. 2022 Sep 15;70:116921. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2022.116921. Epub 2022 Jul 9. Bioorg Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35863237 Review.
-
Human CDC2-like kinase 1 (CLK1): a novel target for Alzheimer's disease.Curr Drug Targets. 2014 May;15(5):539-50. doi: 10.2174/1389450115666140226112321. Curr Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 24568585 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

