Inflammatory Stress Determines the Need for Chemotherapy in Patients with HER2-Positive Esophagogastric Adenocarcinoma Receiving Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
- PMID: 39527097
- PMCID: PMC11788649
- DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-24-0561
Inflammatory Stress Determines the Need for Chemotherapy in Patients with HER2-Positive Esophagogastric Adenocarcinoma Receiving Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
Abstract
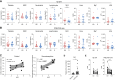
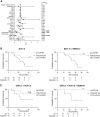
Anti-PD-1, trastuzumab, and chemotherapy are used in the treatment of patients with advanced HER2-positive esophagogastric adenocarcinoma, but long-term survival remains limited. In this study, we report extended follow-up data from the INTEGA trial (NCT03409848), which investigated the efficacy of the anti-PD-1 nivolumab, trastuzumab, and FOLFOX chemotherapy (FOLFOX arm) in comparison with a chemotherapy-free regimen involving nivolumab, trastuzumab, and the anti-CTLA-4 ipilimumab (Ipi arm) in the first-line setting for advanced disease. The 12-month overall survival (OS) showed no statistical difference between the arms, with 57% OS (95% confidence interval, 41%-71%) in the Ipi arm and 70% OS (95% confidence interval, 54%-82%) in the FOLFOX arm. Crossing of the survival curves indicated a potential long-term benefit for some patients within the Ipi arm, but early progressors in the Ipi arm underlined the need for biomarker-guided strategies to optimize treatment selection. To this end, metabolomic and cytokine analyses demonstrated elevated levels of normetanephrine, cortisol, and IL6 in immunotherapy-unresponsive patients in the Ipi arm, suggesting a role for systemic inflammatory stress in modulating antitumor immune responses. Patients with this signature also showed an increased neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio that persisted in the Ipi arm, but not in the FOLFOX arm, and strongly correlated with survival. Furthermore, a low neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio characterized patients benefiting from immunotherapy and targeted therapy without the need for additional chemotherapy. These data suggest that patient selection based on inflammatory stress-driven immune changes could help customize first-line treatment in patients with advanced HER2-positive esophagogastric adenocarcinoma to potentially improve long-term survival.
©2024 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
E. Goekkurt reports grants from Bristol Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from Bristol Myers Squibb outside the submitted work. P. Thuss-Patience reports personal fees from Astellas, MSD, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly and Company, Servier, and Roche, personal fees and nonfinancial support from AstraZeneca, BeiGene, and Daiichi Sankyo, and nonfinancial support from Merck Serono and Celltrion outside the submitted work. T.J. Ettrich reports personal fees from MSD, Roche, Sanofi, Bristol Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, Merck Serono, Pierre Fabre, Servier, Eli Lilly and Company, Ipsen, Daiichi Sankyo, AbbVie, and Takeda, and grants from Eli Lilly and Company and Servier outside the submitted work. A. Reinacher-Schick reports grants from Bristol Myers Squibb and personal fees from Bristol Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study, as well as grants from Roche, BioNTech, and Novartis and personal fees from Roche, Boehringer Ingelheim, Servier, Amgen, MSD, and Pierre Fabre outside the submitted work. D. Pink reports grants and personal fees from PharmaMar and Boehringer Ingelheim and grants from Roche, Deciphera, Recordati, and Bristol Myers Squibb outside the submitted work. C. Bokemeyer reports personal fees from AOK Germany, BioNTech, Lindis Biotech, Sanofi Aventis, med update GmbH, Merck Serono, Roche Pharma, and AstraZeneca and grants and personal fees from Bayer Healthcare outside the submitted work. M. Sinn reports personal fees from Falk and MSD, personal fees and other support from Roche and Pierre Fabre, and other support from Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb, GSK, and Servier outside the submitted work. A. Stein reports grants from Bristol Myers Squibb during the conduct of the study, as well as grants from MSD and BeiGene and other support from Astellas outside the submitted work. M. Binder reports grants from MSD during the conduct of the study. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. . Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Bang Y-J, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, et al. . Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010;376:687–97. - PubMed
-
- Tabernero J, Hoff PM, Shen L, Ohtsu A, Shah MA, Cheng K, et al. . Pertuzumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy for HER2-positive metastatic gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (JACOB): final analysis of a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 2018;19:1372–84. - PubMed
-
- Janjigian YY, Kawazoe A, Bai Y, Xu J, Lonardi S, Metges JP, et al. . Pembrolizumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy for HER2-positive gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma: interim analyses from the phase 3 KEYNOTE-811 randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2023;402:2197–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

