Real-world evidence of effectiveness and safety of pasireotide in the treatment of acromegaly: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39527181
- PMCID: PMC11790789
- DOI: 10.1007/s11154-024-09928-3
Real-world evidence of effectiveness and safety of pasireotide in the treatment of acromegaly: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Real-world evidence of effectiveness and safety of pasireotide in the treatment of acromegaly: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2024 Nov 27. doi: 10.1007/s11154-024-09935-4. Online ahead of print. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2024. PMID: 39602053 No abstract available.
Abstract
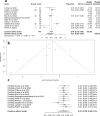
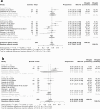
Pasireotide long-acting release (PAS-LAR) is a second-generation somatostatin receptor ligand (SRL) approved for acromegaly treatment. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the real-world effectiveness and safety of PAS-LAR in patients with acromegaly resistant to first-generation somatostatin receptor ligands (fgSRL). A systematic literature search was conducted in PubMed and Web of Science for real-world studies on PAS-LAR in acromegaly published between 2014 and 2023. Random-effects meta-analyses were performed on biochemical control rates, tumor shrinkage, and metabolic parameters. Twelve studies comprising 409 patients were included. The pooled rate of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) control was 57.9% [95% CI: 48.4-66.8] and the percentage of patients with tumor shrinkage was 33.3% [95%CI: 19.7-50.4]. Significant reductions were observed in growth hormone standardized mean difference (SMD) 0.6 ng/mL [95% CI: 0.3 to 1.0] and IGF-1 levels SMD 0.9 ULN [95% CI: 0.4 to 1.4]. However, as expected, a worsening in glucose metabolism was noted as an increase in fasting glucose SMD - 0.8 mg/dL [95% CI: -1.0 to -0.5, p < 0.01], glycated hemoglobin SMD - 0.5% [95% CI: -0.7 to -0.2]. and type 2 diabetes mellitus prevalence SMD - 11.5% (95% CI: -17.5 to -5.5). PAS-LAR demonstrated higher effectiveness in real-world settings, with over 60% of patients achieving IGF-1 control compared to the around 30% efficacy observed in clinical trials. These findings suggest that PAS-LAR is an effective option for acromegaly patients resistant to fgSRL, but careful monitoring of glucose levels is essential. The high heterogeneity observed across studies emphasizes the need for identifying PAS-LAR response biomarkers to set-up individualized treatment approaches for optimizing patient outcomes.
Keywords: Acromegaly; Effectiveness; Hyperglycemia; Pasireotide; Pituitary adenoma; Real world.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Institutional review board statement: Not applicable. Informed consent: Not applicable. Conflict of interest: B.B., MA, MM and M.P.D. have received consulting fees, research support, or participated in clinical trials supported by Pfizer, Ipsen, and/or Recordati. C.T. has received fees for speaker lectures from Gedeon Richte.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Medical Treatments for Acromegaly: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Value Health. 2018 Jul;21(7):874-880. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2017.12.014. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Value Health. 2018. PMID: 30005760
-
Effects of lanreotide SR and Autogel on tumor mass in patients with acromegaly: a systematic review.Pituitary. 2010;13(1):60-7. doi: 10.1007/s11102-009-0169-z. Pituitary. 2010. PMID: 19189218
-
Serum biomarkers of colonic polyps in patients with acromegaly: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Pituitary. 2023 Feb;26(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s11102-022-01287-z. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Pituitary. 2023. PMID: 36542278
-
Predictors of therapeutic failure in GH and prolactin co-secreting pituitary adenomas.Endocr Connect. 2025 Jul 15;14(7):e250103. doi: 10.1530/EC-25-0103. Print 2025 Jul 1. Endocr Connect. 2025. PMID: 40590355 Free PMC article.
-
COMPARATIVE EFFICACY OF MEDICAL TREATMENT FOR ACROMEGALY: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND NETWORK META-ANALYSIS OF INTEGRATED RANDOMIZED TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONAL STUDIES.Endocr Pract. 2020 Apr;26(4):454-462. doi: 10.4158/EP-2019-0528. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Endocr Pract. 2020. PMID: 32045295
Cited by
-
Acromegaly and Cardiovascular Disease: Associated Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Cardiovascular Prognosis, and Therapeutic Impact.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 12;14(6):1906. doi: 10.3390/jcm14061906. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40142714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-Life Data on the Safety of Pasireotide in Acromegaly: Insights from EudraVigilance.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Dec 4;17(12):1631. doi: 10.3390/ph17121631. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39770473 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Impact of Medical Therapies for Acromegaly on Glucose Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 8;26(2):465. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020465. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gross total resection in low-grade and pretreated high-grade invasive growth hormone pituitary adenomas promises favorable outcomes.Discov Oncol. 2025 Aug 1;16(1):1453. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03313-5. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40751108 Free PMC article.
-
Factors affecting disease control after pituitary tumor resection in acromegaly: What is the current evidence?World J Radiol. 2025 Jun 28;17(6):106438. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i6.106438. World J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40606051 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gatto F, Campana C, Cocchiara F, Corica G, Albertelli M, Boschetti M, et al. Current perspectives on the impact of clinical disease and biochemical control on comorbidities and quality of life in acromegaly. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2019;20:365–81. - PubMed
-
- Esposito D, Ragnarsson O, Johannsson G, Olsson DS. Prolonged diagnostic delay in acromegaly is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Eur J Endocrinol. 2020;182:523–31. - PubMed
-
- Giustina A, Barkan A, Beckers A, Biermasz N, Biller BMK, Boguszewski C et al. A Consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of Acromegaly comorbidities: an update. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

