Glutamatergic Circuits in the Pedunculopontine Nucleus Modulate Multiple Motor Functions
- PMID: 39527367
- PMCID: PMC11607253
- DOI: 10.1007/s12264-024-01314-y
Glutamatergic Circuits in the Pedunculopontine Nucleus Modulate Multiple Motor Functions
Abstract
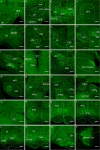
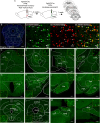
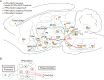
The functional role of glutamatergic (vGluT2) neurons in the pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN) in modulating motor activity remains controversial. Here, we demonstrated that the activity of vGluT2 neurons in the rostral PPN is correlated with locomotion and ipsilateral head-turning. Beyond these motor functions, we found that these rostral PPN-vGluT2 neurons remarkably respond to salient stimuli. Furthermore, we systematically traced the upstream and downstream projections of these neurons and identified two downstream projections from these neurons to the caudal pontine reticular nucleus/anterior gigantocellular reticular nucleus (PnC/GiA) and the zona incerta (ZI). Our findings indicate that the projections to the PnC/GiA inhibit movement, consistent with 'pause-and-play' behavior, whereas those to the ZI promote locomotion, and others respond to a new 'pause-switch-play' pattern. Collectively, these findings elucidate the multifaceted influence of the PPN on motor functions and provide a robust theoretical framework for understanding its physiological and potential therapeutic implications.
Keywords: Anterior gigantocellular reticular nucleus; Caudal pontine reticular nucleus; Glutamatergic neuron; Pause-and-play; Pedunculopontine nucleus; Zona incerta.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Shik ML, Severin FV, Orlovskiĭ GN. Control of walking and running by means of electric stimulation of the midbrain. Biofizika 1966, 11: 659–666. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

