INHIBITING SIRT2 ATTENUATES SEPSIS-INDUCED ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY VIA FOXO1 ACETYLATION-MEDIATED AUTOPHAGY ACTIVATION
- PMID: 39527461
- PMCID: PMC11776882
- DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002505
INHIBITING SIRT2 ATTENUATES SEPSIS-INDUCED ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY VIA FOXO1 ACETYLATION-MEDIATED AUTOPHAGY ACTIVATION
Abstract
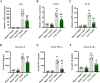
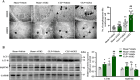
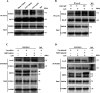
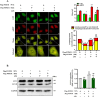
Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (SAKI), a common complication in intensive care units (ICUs), is linked to high morbidity and mortality. Sirtuin 2 (SIRT2), an NAD + -dependent deacetylase, has been shown to have distinct effects on autophagy regulation compared to other sirtuins, but its role in SAKI remains unclear. This study explored the potential of SIRT2 as a therapeutic target for SAKI. We found that inhibition of SIRT2 with the antagonist AGK2 improved the survival of septic mice. SIRT2 inhibition reduced kidney injury, as indicated by lower levels of KIM-1, NGAL, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, and proinflammatory cytokines following cecal ligation and puncture. Pretreatment with AGK2 in septic mice increased autophagosome and autolysosome formation in renal tubular epithelial cells and upregulated LC3 II expression in the renal cortex. Consistent with in vivo findings, SIRT2 gene silencing promoted autophagy in LPS-treated HK-2 cells, whereas SIRT2 overexpression inhibited it. Mechanistically, SIRT2 inhibition increased FOXO1 acetylation, inducing its nuclear-to-cytoplasmic translocation, which promoted kidney autophagy and alleviated SAKI. Our study suggests SIRT2 as a potential target for SAKI therapy.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Shock Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
p53 Deacetylation Alleviates Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Promoting Autophagy.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 14;12:685523. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.685523. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34335587 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 attenuates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via Beclin1 deacetylation-mediated autophagy activation.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Feb 26;12(2):217. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03508-y. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33637691 Free PMC article.
-
Zn2+ improves sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by upregulating SIRT7-mediated Parkin acetylation.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Jul 1;327(1):F184-F197. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00337.2023. Epub 2024 May 23. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38779758
-
SIRT2 inhibition attenuates myofibroblast transition through autophagy-mediated ciliogenesis in renal epithelial cells.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2025 Apr;181:106754. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2025.106754. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39988243
-
[The advances on autophagy the pathogenesis and treatment in septic acute kidney injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025 Feb;37(2):183-187. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20240904-00748. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2025. PMID: 40017369 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Klotho plasma levels are an independent predictorof mortality in women with acute coronary syndrome.Sci Rep. 2025 May 14;15(1):16744. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01334-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40369094 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms and functions of protein acetylation in sepsis and sepsis-associated organ dysfunction.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jul 26;30(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00773-z. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40713493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CREATINE KINASE IS ELEVATED BY THE SUBMANDIBULAR VEIN BLEED TECHNIQUE, OBSCURING THE MEASUREMENT OF MUSCLE DAMAGE IN SEPSIS.Shock. 2025 Jun 1;63(6):944-946. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002585. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Shock. 2025. PMID: 40367917 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

