Functional identification of soluble uric acid as an endogenous inhibitor of CD38
- PMID: 39527634
- PMCID: PMC11554305
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.96962
Functional identification of soluble uric acid as an endogenous inhibitor of CD38
Abstract
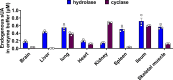
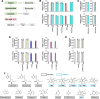
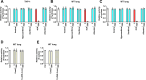
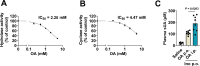
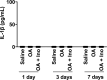
Excessive elevation or reduction of soluble uric acid (sUA) levels has been linked to some of pathological states, raising another subject that sUA at physiological levels may be essential for the maintenance of health. Yet, the fundamental physiological functions and molecular targets of sUA remain largely unknown. Using enzyme assays and in vitro and in vivo metabolic assays, we demonstrate that sUA directly inhibits the hydrolase and cyclase activities of CD38 via a reversible non-competitive mechanism, thereby limiting nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) degradation. CD38 inhibition is restricted to sUA in purine metabolism, and a structural comparison using methyl analogs of sUA such as caffeine metabolites shows that 1,3-dihydroimidazol-2-one is the main functional group. Moreover, sUA at physiological levels prevents crude lipopolysaccharide (cLPS)-induced systemic inflammation and monosodium urate (MSU) crystal-induced peritonitis in mice by interacting with CD38. Together, this study unveils an unexpected physiological role for sUA in controlling NAD+ availability and innate immunity through CD38 inhibition, providing a new perspective on sUA homeostasis and purine metabolism.
Keywords: CD38; MSU crystal; gout; hyperuricemia; hypouricemia; immunology; inflammation; metabolism; mouse; nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; uric acid; uricase.
© 2024, Wen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SW, HA, SY, YS, HH, IT No competing interests declared
Figures

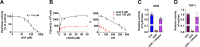




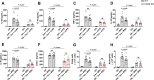
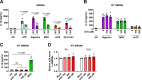


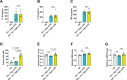
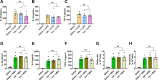

Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2023.06.03.543541
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.96962.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.96962.2
Similar articles
-
CD38 activation by monosodium urate crystals contributes to inflammatory responses in human and murine macrophages.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Dec 3;581:6-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.10.010. Epub 2021 Oct 7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 34637964
-
The NADase CD38 is a central regulator in gouty inflammation and a novel druggable therapeutic target.Inflamm Res. 2024 May;73(5):739-751. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01863-y. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38493256 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Role of Astrocyte NAD+ Glycohydrolase in Myelin Injury and Regeneration.J Neurosci. 2021 Oct 13;41(41):8644-8667. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2264-20.2021. Epub 2021 Sep 7. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34493542 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CD38 in Adipose Tissue: Tuning Coenzyme Availability?Nutrients. 2021 Oct 23;13(11):3734. doi: 10.3390/nu13113734. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34835990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CD38 glycohydrolase and the NAD sink: implications for pathological conditions.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Mar 1;322(3):C521-C545. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00451.2021. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35138178 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

