Subchronic elevation in ambient temperature drives alterations to the sperm epigenome and accelerates early embryonic development in mice
- PMID: 39527742
- PMCID: PMC11588121
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2409790121
Subchronic elevation in ambient temperature drives alterations to the sperm epigenome and accelerates early embryonic development in mice
Abstract
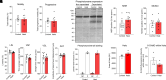
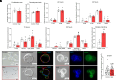
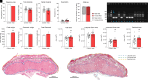
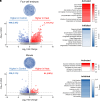
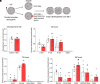
Forecasted increases in the prevalence and severity of extreme weather events accompanying changes in climatic behavior pose potential risk to the reproductive capacity of humans and animals of ecological and agricultural significance. While several studies have revealed that heat stress induced by challenges such as testicular insulation can elicit a marked negative effect on the male reproductive system, and particularly the production of spermatozoa, less is known about the immediate impact on male reproductive function following subchronic whole-body exposure to elevated ambient temperature. To address this knowledge gap, we exposed unrestrained male mice to heat stress conditions that emulate a heat wave (daily cycle of 8 h at 35 °C followed by 16 h at 25 °C) for a period of 7 d. Neither the testes or epididymides of heat-exposed male mice exhibited evidence of gross histological change, and similarly, spermatozoa of exposed males retained their functionality and ability to support embryonic development. However, the embryos generated from heat-exposed spermatozoa experienced pronounced changes in gene expression linked to acceleration of early embryo development, aberrant blastocyst hatching, and increased fetal:placental weight ratio. Such changes were causally associated with an altered sperm small noncoding RNA (sncRNA) profile, such that these developmental phenotypes were recapitulated by microinjection of wild-type embryos sired by control spermatozoa with RNAs extracted from heat-exposed spermatozoa. Such data highlight that even relatively modest excursions in ambient temperature can affect male reproductive function and identify the sperm sncRNA profile as a particular point of vulnerability to this imposed environmental stress.
Keywords: embryo development; epididymis; heat; small non-protein-coding RNA; sperm.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report, Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Pachauri R. K., Meyer L. A., Eds. (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Geneva, Switzerland, 2014), p. 151.
-
- Robinson P. J., On the definition of a heat wave. J. Appl. Meteorol. 40, 762–775 (2001).
-
- Nienaber J. A., Hahn G. L., Brown-Brandl T. M., Eigenberg R. A., “Summer heat waves–Extreme years” in 2007 ASAE Annual Meeting (American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, 2007).
-
- Nidumolu U., et al. , Spatio-temporal modelling of heat stress and climate change implications for the Murray dairy region, Australia. Int. J. Biometeorol. 58, 1095–1108 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

