Elevated serum growth differentiation factor 15 and decorin predict the fibrotic progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
- PMID: 39528512
- PMCID: PMC11554648
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-77719-6
Elevated serum growth differentiation factor 15 and decorin predict the fibrotic progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease
Abstract
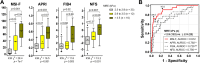
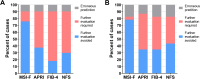
Mitochondrial dysfunction with oxidative stress contributes to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) progression. We aimed to evaluate the fibrosis predictive efficacy of a novel non-invasive diagnostic panel using metabolic stress biomarkers. From a population-based general cohort, 144 subjects with MASLD were recruited in the development group and underwent magnetic resonance imaging-based liver examinations, anthropometric and laboratory tests. As an external validation group, 41 patients enrolled in a biopsy-evaluated MASLD cohort participated in this study. Liver fat content and stiffness were measured by magnetic resonance (MR) imaging-proton density fat fraction and MR elastography (MRE), respectively. Serologic stress biomarkers were quantitated by ELISA. Multivariate regression showed that waist-to-height ratio, growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF15), γ-glutamyltransferase, decorin, and alkaline-phosphatase were independent predictors of hepatic fibrosis (rank-ordered by Wald). The area under receiver-operator characteristics curve [AUROC (95% CI)) of the metabolic stress index for fibrosis (MSI-F) was 0.912 (0.85‒0.98) and 0.977 (0.92‒1.00) in development and validation groups, respectively. MSI-F also had better diagnostic accuracy (82.6‒92.4%) than other fibrosis indices in the both study cohorts. MSI-F consistently differentiated fibrosis severities across cohorts of MRE-evaluated general population and biopsy-proven patients with MASLD, while other indices showed no or less discrimination. MSI-F, as a novel non-invasive index based on a stress-stimulated protective hormone GDF15 and decorin, effectively predicted hepatic fibrosis. Furthermore, MSI-F may serve as pre-screening tool to increase the population that could be excluded from further evaluation, reducing unnecessary invasive investigations more effectively than other indices.
Keywords: Decorin; Growth differentiation factor-15; Hepatic fibrosis; Mitochondrial stress; Serum biomarker.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
A combination of non-invasive tests for the detection of significant fibrosis in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease is not superior to magnetic resonance elastography alone.Eur Radiol. 2024 Jun;34(6):3882-3888. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10441-5. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37987833
-
Metabolic Stress Index Including Mitochondrial Biomarker for Noninvasive Diagnosis of Hepatic Steatosis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 19;13:896334. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.896334. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35663311 Free PMC article.
-
Serum growth differentiation factor 15 is a novel biomarker with high predictive capability for liver cancer occurrence in patients with MASLD regardless of liver fibrosis.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Aug;60(3):327-339. doi: 10.1111/apt.18063. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38828944
-
Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis through Noninvasive Tests in Steatotic Liver Disease.Korean J Gastroenterol. 2024 Nov 25;84(5):215-222. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2024.103. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39582309 Review.
-
Role of noninvasive tests in the prognostication of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2025 Feb;31(Suppl):S51-S75. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0246. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 38934108 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual signaling pathways of TGF-β superfamily cytokines in hepatocytes: balancing liver homeostasis and disease progression.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 7;16:1580500. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1580500. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40260391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disease-Specific Novel Role of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in Organ Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 14;26(12):5713. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125713. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565178 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Starley, B. Q., Calcagno, C. J. & Harrison, S. A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma: a weighty connection. Hepatology51(5), 1820–1832 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Wong, V. W., Adams, L. A., de Ledinghen, V., Wong, G. L. & Sookoian, S. Noninvasive biomarkers in NAFLD and NASH - current progress and future promise. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.15(8), 461–478 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Tilg, H. & Moschen, A. R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology52(5), 1836–1846 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Karkucinska-Wieckowska, A. et al. Mitochondria, oxidative stress and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A complex relationship. Eur. J. Clin. Investig.52(3), e13622 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

