Discovery of miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks in glioblastoma reveals novel insights into tumor microenvironment remodeling
- PMID: 39528571
- PMCID: PMC11555236
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-78337-y
Discovery of miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks in glioblastoma reveals novel insights into tumor microenvironment remodeling
Abstract
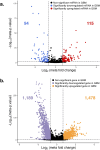
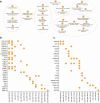
Adult glioblastoma (GBM) is a highly aggressive primary brain tumor, accounting for nearly half of all malignant brain tumors, with a median survival rate of only 8 months. Treatment for GBM is largely ineffective due to the highly invasive nature and complex tumor composition of this malignancy. MicroRNAs (miRNA) are short, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression by binding to messenger RNAs (mRNA). While specific miRNA have been associated with GBM, their precise roles in tumor development and progression remain unclear. In this study, the analysis of miRNA expression data from 743 adult GBM cases and 59 normal brain samples identified 94 downregulated miRNA and 115 upregulated miRNA. Many of these miRNA were previously linked to GBM pathology, confirming the robustness of our approach, while we also identified novel miRNA that may act as potential regulators in GBM. By integrating miRNA predictions with gene expression data, we were able to associate downregulated miRNA with tumor microenvironment factors, including extracellular matrix remodeling and signaling pathways involved in tumor initiation, while upregulated miRNA were found to be associated with essential neuronal processes. This analysis highlights the significance of miRNA in GBM and serves as a foundation for further investigation.
Keywords: Extracellular matrix; Glioblastoma; Growth signaling; Tumor microenvironment; microRNA.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of prognostic biomarkers in glioblastoma using a long non-coding RNA-mediated, competitive endogenous RNA network.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 5;7(27):41737-41747. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9569. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27229531 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA-associated ceRNA network reveals novel potential prognostic regulatory axes in glioblastoma multiforme.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jun;28(11):e18392. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18392. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38864705 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA profile of glioblastoma reveals the potential role of lncRNAs in contributing to glioblastoma pathogenesis.Int J Oncol. 2012 Jun;40(6):2004-12. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1413. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22446686
-
Targeting strategies on miRNA-21 and PDCD4 for glioblastoma.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 Aug 15;580:64-74. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.07.001. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 26142886 Review.
-
Natural flavonoids alleviate glioblastoma multiforme by regulating long non-coding RNA.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 May;161:114477. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114477. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36931030 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Deregulated miRNAs and mRNAs Involved in Tumorigenesis and Detection of Glioblastoma Patients Applying Next-Generation RNA Sequencing.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Mar 19;18(3):431. doi: 10.3390/ph18030431. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40143207 Free PMC article.
-
What Epigenetics Teaches Us About Neuron-Glioma Interactions.Bioessays. 2025 Sep;47(9):e70043. doi: 10.1002/bies.70043. Epub 2025 Jul 20. Bioessays. 2025. PMID: 40685688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Deep Differential Analysis in Four Subtypes of Breast Cancer Based on Regulations of miRNA-mRNA.IET Syst Biol. 2025 Jan-Dec;19(1):e70020. doi: 10.1049/syb2.70020. IET Syst Biol. 2025. PMID: 40498676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bao, S. et al. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature444, 756–760 (2006). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

