Prediction of miRNA-disease association based on multisource inductive matrix completion
- PMID: 39528650
- PMCID: PMC11555322
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-78212-w
Prediction of miRNA-disease association based on multisource inductive matrix completion
Abstract
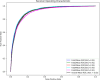
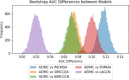
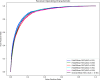
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous non-coding RNAs approximately 23 nucleotides in length, playing significant roles in various cellular processes. Numerous studies have shown that miRNAs are involved in the regulation of many human diseases. Accurate prediction of miRNA-disease associations is crucial for early diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis assessment of diseases. In this paper, we propose the Autoencoder Inductive Matrix Completion (AEIMC) model to identify potential miRNA-disease associations. The model captures interaction features from multiple similarity networks, including miRNA functional similarity, miRNA sequence similarity, disease semantic similarity, disease ontology similarity, and Gaussian interaction kernel similarity between miRNAs and diseases. Autoencoders are used to extract more complex and abstract data representations, which are then input into the inductive matrix completion model for association prediction. The effectiveness of the model is validated through cross-validation, stratified threshold evaluation, and case studies, while ablation experiments further confirm the necessity of introducing sequence and ontology similarities for the first time.
Keywords: Ablation experiment; Autoencoder; Inductive matrix completion; Multi-source information; Optimization algorithm; miRNA-disease association.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


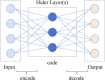

Similar articles
-
Predicting miRNA-Disease Association Based on Neural Inductive Matrix Completion with Graph Autoencoders and Self-Attention Mechanism.Biomolecules. 2022 Jan 2;12(1):64. doi: 10.3390/biom12010064. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35053212 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting miRNA-disease association based on inductive matrix completion.Bioinformatics. 2018 Dec 15;34(24):4256-4265. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty503. Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29939227
-
SNFIMCMDA: Similarity Network Fusion and Inductive Matrix Completion for miRNA-Disease Association Prediction.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 9;9:617569. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.617569. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33634120 Free PMC article.
-
DNRLMF-MDA:Predicting microRNA-Disease Associations Based on Similarities of microRNAs and Diseases.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2019 Jan-Feb;16(1):233-243. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2017.2776101. Epub 2017 Nov 22. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 29990253
-
An improved random forest-based computational model for predicting novel miRNA-disease associations.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Dec 3;20(1):624. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-3290-7. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31795954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hua, S., Yun, W., Zhiqiang, Z. & Zou, Q. A discussion of micrornas in cancers. Curr. Bioinform.9, 453–462. 10.2174/1574893609666140804221135 (2014).
-
- Lynam-Lennon, N., Maher, S. G. & Reynolds, J. V. The roles of microRNA in cancer and apoptosis. Biol. Rev.84, 55–71. 10.1111/j.1469-185X.2008.00061.x (2009). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

