Mechanism for Vipp1 spiral formation, ring biogenesis, and membrane repair
- PMID: 39528797
- PMCID: PMC11919738
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-024-01401-8
Mechanism for Vipp1 spiral formation, ring biogenesis, and membrane repair
Abstract
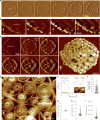
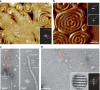
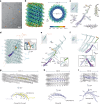
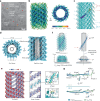
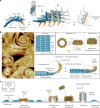
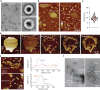
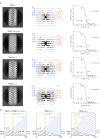
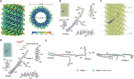
The ESCRT-III-like protein Vipp1 couples filament polymerization with membrane remodeling. It assembles planar sheets as well as 3D rings and helical polymers, all implicated in mitigating plastid-associated membrane stress. The architecture of Vipp1 planar sheets and helical polymers remains unknown, as do the geometric changes required to transition between polymeric forms. Here we show how cyanobacterial Vipp1 assembles into morphologically-related sheets and spirals on membranes in vitro. The spirals converge to form a central ring similar to those described in membrane budding. Cryo-EM structures of helical filaments reveal a close geometric relationship between Vipp1 helical and planar lattices. Moreover, the helical structures reveal how filaments twist-a process required for Vipp1, and likely other ESCRT-III filaments, to transition between planar and 3D architectures. Overall, our results provide a molecular model for Vipp1 ring biogenesis and a mechanism for Vipp1 membrane stabilization and repair, with implications for other ESCRT-III systems.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The cyanobacterial protein VIPP1 forms ESCRT-III-like structures on lipid bilayers.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025 Mar;32(3):543-554. doi: 10.1038/s41594-024-01367-7. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39060677 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Vipp1 and PspA are members of the ancient ESCRT-III membrane-remodeling superfamily.Cell. 2021 Jul 8;184(14):3660-3673.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.041. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Cell. 2021. PMID: 34166615 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for VIPP1 oligomerization and maintenance of thylakoid membrane integrity.Cell. 2021 Jul 8;184(14):3643-3659.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.011. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Cell. 2021. PMID: 34166613
-
Conserved structures of ESCRT-III superfamily members across domains of life.Trends Biochem Sci. 2023 Nov;48(11):993-1004. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2023.08.009. Epub 2023 Sep 15. Trends Biochem Sci. 2023. PMID: 37718229 Review.
-
The role of VPS4 in ESCRT-III polymer remodeling.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Feb 28;47(1):441-448. doi: 10.1042/BST20180026. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 30783012 Review.
Cited by
-
Thylakoid membrane remodeling by VIPP1 ESCRT-III-like filaments.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025 Mar;32(3):414-417. doi: 10.1038/s41594-025-01511-x. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40102625 Free PMC article.
-
The thylakoid membrane remodeling protein VIPP1 forms bundled oligomers in tobacco chloroplasts.Plant Physiol. 2025 Apr 30;198(1):kiaf137. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiaf137. Plant Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40198871 Free PMC article.
-
The green ESCRTs: Newly defined roles for ESCRT proteins in plants.J Biol Chem. 2025 May;301(5):108465. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108465. Epub 2025 Mar 27. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40157538 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu, J. et al. Functional assignment of multiple ESCRT‐III homologs in cell division and budding in Sulfolobus islandicus. Mol. Microbiol.105, 540–553 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Juan, T. & Fürthauer, M. Biogenesis and function of ESCRT-dependent extracellular vesicles. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol.74, 66–77 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

