Benchmark of screening markers for KEAP1/NFE2L2 mutations and joint analysis with the K1N2-score
- PMID: 39528799
- PMCID: PMC11554772
- DOI: 10.1038/s41698-024-00744-1
Benchmark of screening markers for KEAP1/NFE2L2 mutations and joint analysis with the K1N2-score
Abstract
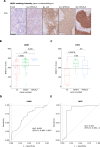
Our recently published K1N2-score robustly predicts KEAP1/NFE2L2-mutations and pathway activation status, while its accessibility might be limited. We tested if the RNA expression data of six pathway-related genes and NQO1-IHC might be a reliable alternative using 348 KEAP1/NFE2L2 mutation-enriched NSCLC. While TXNRD1 RNA testing was the best-performing single-gene test, the combination of single-gene screening and validation with the K1N2-score achieved the highest performance when predicting mutation status or pathway activation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Nadal, E., Palmero, R. & Muñoz-Pinedo, C. Mutations in the antioxidant KEAP1/NRF2 pathway define an aggressive subset of NSCLC resistant to conventional treatments. J. Thorac. Oncol. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer14, 1881–1883 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Goeman, F. et al. Mutations in the KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway define a molecular subset of rapidly progressing lung adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer14, 1924–1934 (2019). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

