Association of serum albumin-to-creatinine ratio with in-hospital mortality in patients with severe acute pancreatitis: a retrospective study
- PMID: 39529034
- PMCID: PMC11552424
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-024-03493-4
Association of serum albumin-to-creatinine ratio with in-hospital mortality in patients with severe acute pancreatitis: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: The serum albumin-to-serum creatinine ratio (sACR) is independently associated with the prognosis of multiple diseases. However, its relationship with in-hospital mortality of patients with severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) remains unclear.
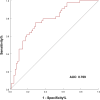
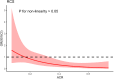
Methods: Patients diagnosed with SAP between April 2016 and December 2023 were collected. These patients were categorized into low and high sACR groups based on an optimal cut-off value calculated using Youden's index. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was utilized to examine the relationship between sACR levels and the in-hospital mortality. Additionally, a limited restricted cubic spline (RCS) method was employed to evaluate the nonlinear relationship between sACR values and the risk of in-hospital mortality. The potential for unmeasured confounders between sACR levels and in-hospital mortality was also explored through the calculation of the E value.
Results: A total of 114 eligible patients were included in this sutdy. The multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated an independent association between sACR levels and in-hospital mortality (p < 0.001). The RCS analysis demonstrated a linear correlation between sACR values and the risk of in-hospital mortality (P for non-linearity > 0.05), where the risk increased as the sACR value decreased.
Conclusions: The research findings suggest that sACR levels are independently associated with in-hospital mortality of patients with SAP, providing a means for early identification of those at high risk of in-hospital mortality. This early identification may facilitate the optimizing and strengthening of treatments, ultimately leading to improved outcomes.
Keywords: In-hospital mortality; Serum albumin-to-serum creatinine ratio; Severe acute pancreatitis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association between serum albumin creatinine ratio and all-cause mortality in intensive care unit patients with heart failure.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jul 4;11:1406294. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1406294. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39027002 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Serum Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio and Readmission in Elderly Heart Failure Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Gerontology. 2025;71(1):28-38. doi: 10.1159/000542616. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Gerontology. 2025. PMID: 39557035
-
Prognostic value of serum albumin-to-creatinine ratio in patients with acute myocardial infarction: Results from the retrospective evaluation of acute chest pain study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Aug 28;99(35):e22049. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022049. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32871964 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Albumin-To-Creatinine Ratio With Diabetic Retinopathy Among US Adults (NHANES 2009-2016).Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2025 Jan;8(1):e70029. doi: 10.1002/edm2.70029. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2025. PMID: 39826101 Free PMC article.
-
Association between serum creatinine to albumin ratio and short- and long-term all-cause mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis admitted to the intensive care unit: a retrospective analysis based on the MIMIC-IV database.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 15;15:1373371. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1373371. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38686375 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prognostic value of serum albumin-creatinine ratio as a biomarker in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.Immunotherapy. 2025 Jun;17(8):567-575. doi: 10.1080/1750743X.2025.2513850. Epub 2025 Jun 5. Immunotherapy. 2025. PMID: 40470574
-
Phospholipase D2: A biomarker implicated in various pancreatic diseases beyond acute pancreatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jul 28;31(28):108271. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i28.108271. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40741474 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Albumin-Creatinine Ratio and Anthracycline Cardiotoxicity in Patients with Cancer.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 5;14(5):1741. doi: 10.3390/jcm14051741. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40095884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee PJ, Papachristou GI. New insights into acute pancreatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:479–96. - PubMed
-
- Iannuzzi JP, King JA, Leong JH, et al. Global incidence of Acute Pancreatitis is increasing over time: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2022;162:122–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

