Anti-hypertensives associated with survival in cancer patients receiving immunotherapy: new evidence from a real-world cohort study and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39529892
- PMCID: PMC11552054
- DOI: 10.1177/17588359241292227
Anti-hypertensives associated with survival in cancer patients receiving immunotherapy: new evidence from a real-world cohort study and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in cancer patients taking anti-hypertensive drugs is still not well established.
Objective: To elucidate the effect of anti-hypertensive drugs on the clinical outcome of cancer patients receiving immunotherapy.
Design: A retrospective cohort study and meta-analysis.
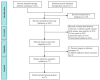
Method: We conducted a real-world retrospective study of cancer patients treated with immunotherapy at two tertiary centers between January 2019 and June 2023, with primary outcomes being overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). In addition, we performed a meta-analysis to synthesize currently relevant clinical studies.
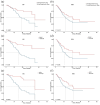
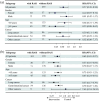
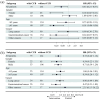
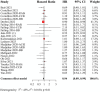
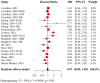
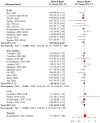
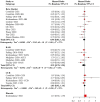
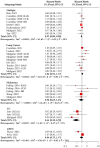
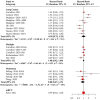
Results: A retrospective clinical study of 336 patients from 2 centers suggested that the use of anti-hypertensive drugs was related to a preferable OS (hazard ratio (HR) = 0.55, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.33-0.90) compared to non-users. For PFS, no significant correlation was detected (HR = 0.71, 95% CI: 0.49-1.03). Further analysis revealed that renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (RASi) and calcium channel blocker (CCB) have a synergistic effect with ICIs. In addition, subgroup analysis found that the benefits of RASi or CCB in combination with ICIs are greater in women or patients ⩾65 years of age. There was better disease control in lung cancer patients using RASi, and a significantly longer OS was observed in patients with gastrointestinal tumors taking CCB. Meta-analysis suggested that anti-hypertensive drugs were associated with improved OS, but only the combination of RASi and immunotherapy showed a synergistic effect. No significant correlation with OS was found for other anti-hypertensive drugs, and there was no overall positive effect on PFS.
Conclusion: Our study found that use of anti-hypertensive drugs, particularly RASi or CCB, was associated with improved OS in patients undergoing immunotherapy. The synergistic effects of RASi or CCB with ICIs were more pronounced in females or elderly. RASi or CCB exhibited different benefits in various types of tumors. These findings provide valuable insights for treating cancer patients with hypertension.
Keywords: anti-hypertensive drugs; calcium channel blocker; cancer survival; immune checkpoint inhibitors; renin–angiotensin system inhibitor.
© The Author(s), 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of early initiation of renin-angiotensin blockade on renal function and clinical outcomes in patients with hypertensive emergency: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2023 Mar 22;24(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03117-1. BMC Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36949416 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on outcomes in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with immune-checkpoint inhibitors.Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2022 Aug;20(4):301-306. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2022.04.012. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35614012 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors on survival outcomes in cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 19;14:1155104. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1155104. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37153578 Free PMC article.
-
Novel evidence for the prognostic impact of β-blockers in solid cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Dec;113(Pt A):109383. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109383. Epub 2022 Oct 28. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36330916
-
Calcium channel blocker monotherapy versus combination with renin-angiotensin system inhibitors on the development of new-onset diabetes mellitus in hypertensive Korean patients.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2019 Jun;16(6):439-447. doi: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2019.06.003. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31308836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luke JJ, Ascierto PA, Carlino MS, et al.. KEYNOTE-716: phase III study of adjuvant pembrolizumab versus placebo in resected high-risk stage II melanoma. Future Oncol 2020; 16: 4429–4438. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

