Self-puberty staging in endocrine encounters during the COVID pandemic
- PMID: 39530119
- PMCID: PMC11550967
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1487329
Self-puberty staging in endocrine encounters during the COVID pandemic
Abstract
Background: Evaluation of pubertal development is crucial in Endocrinology. The rise in telemedicine during COVID-19 has made conduct of physical examinations more challenging, especially for pubertal assessment. Previous studies on validity of pubertal self-staging versus clinical examination have yielded mixed results. This study aimed to determine validity and reliability of self-staging of puberty, with potential application during telemedicine visits. The present study is the first to assess pediatric self-rated pubertal staging during the pandemic.
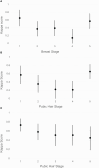
Methods: The study included patients aged 7-22 years referred to Pediatric Endocrinology for specialty care, including pubertal staging. At clinic check-in, patients received a packet with study description, an option to "opt in" or "opt out", sex-specific self-staging instructions, and Tanner (T) stage illustrations. Males received materials for pubic hair (PH) stages T1-T5; females received materials for PH and breast (BR) stages T1-T5. Patients who opted in had 10 minutes to select the image(s) that best matched their bodies, which they sealed in an envelope. This was followed by a clinic visit, where a board-certified pediatric endocrinologist conducted a physical examination, including breast staging (females), testicular size measurement (males), and pubic hair staging (both sexes). Pubertal stage Kappa statistics with 95% CI were calculated for each body part by sex, with Kappa ≥ 0.60 indicating significant agreement between self-assessment and physician assessment (0.40-0.60 moderate; 0.20-0.40 fair).
Results: Of 516 distributed packets, 243 self-assessments (125 females) were returned, with 81% (94 females/102 males) being complete (including pediatric endocrinologist staging). Mean age of participants was 12.8 years. Mean BMI was 22.2 kg/m² (males) and 23.7 kg/m² (females). Hypothyroidism was the most common endocrine diagnosis. For females, kappa was highest for BR and PH in T1 (BR 0.65, PH 0.57) and T5 (BR 0.57, PH 0.65). For males, kappa was highest in T1 (0.73) and T2 (0.58). Grouping Tanner stages into prepuberty (T1), early to mid-puberty (T2-T3), and late puberty (T4-T5) showed greater agreement.
Conclusion: Patients can reliably distinguish between "puberty" and "no puberty" using self-staging, though differentiating between later pubertal stages is more challenging. These findings help define the utility and limitations of self-staging during telemedicine visits.
Keywords: COVID; puberty; self-staging; tanner stage; telemedicine.
Copyright © 2024 Ebo, McCray, Bowers, Rose and Jones.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Breehl L. Physiology, puberty, StatPearls (2023). Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534827/ (Accessed 06 June 2024). - PubMed
-
- Weber G, Vigone MC, Stroppa L, Chiumello G. Thyroid function and puberty. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. (2003) 16:253–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

