JCCG ALL-B12: Evaluation of Intensified Therapies With Vincristine/Dexamethasone Pulses and Asparaginase and Augmented High-Dose Methotrexate for Pediatric B-ALL
- PMID: 39531610
- PMCID: PMC11809717
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.24.00811
JCCG ALL-B12: Evaluation of Intensified Therapies With Vincristine/Dexamethasone Pulses and Asparaginase and Augmented High-Dose Methotrexate for Pediatric B-ALL
Abstract
Purpose: The JCCG ALL-B12 clinical trial aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of unvalidated treatment phases for pediatric ALL and develop a safety-focused treatment framework.
Patients and methods: Patients age 1-19 years with newly diagnosed B-ALL were enrolled in this study. These patients were stratified into standard-risk (SR), intermediate-risk (IR), and high-risk (HR) groups. Randomized comparisons assessed the effectiveness of vincristine (VCR)/dexamethasone pulses in the SR group, evaluated the effects of L-asparaginase (ASP) intensification in the IR group, and compared standard consolidation including block-type treatment with experimental consolidation with high-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX) intensified with VCR and ASP in the HR group.
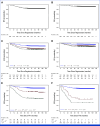
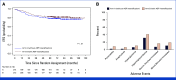
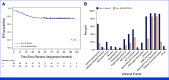
Results: Of 1,936 patients enrolled, 1,804 were eligible for the experimental treatment. The overall 5-year event-free survival and overall survival rates were 85.2% (95% CI, 83.5 to 86.8) and 94.3% (95% CI, 93.1 to 95.3), respectively. The cumulative incidence of relapse and postremission nonrelapse mortality was 13.2% (95% CI, 11.6 to 14.8) and 0.6% (95% CI, 0.3 to 1.0), respectively. Random assignment in the SR group showed no significant benefit from pulse therapy. In the IR group, ASP intensification had limited effects. In the HR group, standard block therapy and HD-MTX yielded equivalent outcomes.
Conclusion: The ALL-B12 trial achieved favorable outcomes in a nationwide cohort by stratifying treatment on the basis of risk and balancing treatment intensity. This study not only demonstrated that existing standard of care can be further refined but also indicated that improvement in outcomes with intensified chemotherapy has reached a plateau.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures


References
-
- Ariffin H, Chiew EKH, Oh BLZ, et al. : Anthracycline-free protocol for favorable-risk childhood ALL: A noninferiority comparison between Malaysia-Singapore ALL 2003 and ALL 2010 studies. J Clin Oncol 41:3642-3651, 2023 - PubMed
-
- Brown PA, Ji L, Xu X, et al. : Effect of postreinduction therapy consolidation with blinatumomab vs chemotherapy on disease-free survival in children, adolescents, and young adults with first relapse of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 325:833-842, 2021 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

