Effectiveness evaluation of an organisational intervention, targeting pregnancy and addiction care professionals, among women who have just given birth in maternity wards and smoked tobacco during pregnancy (5A-QUIT-N): study protocol for a stepped-wedge cluster randomised trial
- PMID: 39532364
- PMCID: PMC11575246
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-087541
Effectiveness evaluation of an organisational intervention, targeting pregnancy and addiction care professionals, among women who have just given birth in maternity wards and smoked tobacco during pregnancy (5A-QUIT-N): study protocol for a stepped-wedge cluster randomised trial
Abstract
Introduction: In 2021, among French women who smoked when they knew they were pregnant, 59% still smoked at the end of pregnancy. Support for pregnant women to stop smoking must include a structured organisational perspective. The main objective of the study is to evaluate the effectiveness of the 5A-QUIT-N organisational intervention on smoking cessation at delivery among pregnant women who smoke during pregnancy.
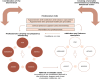
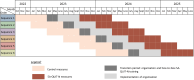
Methods and analysis: The overarching goal of the 5A-QUIT-N intervention, which aims to organise the healthcare professionals monitoring pregnancy, specialists in addiction and tobacco use, and clinical and training tools, using the 5As method. The 5A-QUIT-N intervention will be evaluated in a pragmatic stepped-wedge cluster randomised trial. Within each cluster, during the 6 months before (control) and after (intervention) the intervention, women who smoke tobacco during pregnancy will be enrolled during their maternity stay after delivery. A transition period is planned between the control and intervention periods to deploy the intervention. All participating women will be interviewed using a heteroquestionnaire to assess smoking cessation, tobacco use monitoring by healthcare professionals and individual factors associated with tobacco use during pregnancy. The primary outcome was the point prevalence of abstinence at delivery, which is the proportion of women reporting abstinence from smoking for at least 7 days at delivery. 4200 women who smoked tobacco during pregnancy will be recruited over the entire study period (33 months) to evaluate the effectiveness. An estimated 4585 participants will be included for all aims.
Ethics and dissemination: The study will be implemented in accordance with French regulations. The study including the consent process has been independently reviewed and approved by the French ethical board 'CPP Ile de France I' on 10 February 2022 (No CPPIDF1-2022-DI08-cat.2). The results will be disseminated on various academic and non-academic platforms. The results will be reported in international peer-reviewed journals and presented at international and national conferences.
Keywords: Organisation of health services; Pregnancy; Psychosocial Intervention; Randomized Controlled Trial; Tobacco Use.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Indigenous Counselling and Nicotine (ICAN) QUIT in Pregnancy Pilot Study protocol: a feasibility step-wedge cluster randomised trial to improve health providers' management of smoking during pregnancy.BMJ Open. 2017 Aug 4;7(8):e016095. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016095. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28780551 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Protocol for study of financial incentives for smoking cessation in pregnancy (FISCP): randomised, multicentre study.BMJ Open. 2016 Jul 26;6(7):e011669. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011669. BMJ Open. 2016. PMID: 27466239 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of implementation strategies on the routine provision of antenatal care addressing smoking in pregnancy: study protocol for a non-randomised stepped-wedge cluster controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2024 Apr 5;14(4):e076725. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-076725. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38580367 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for waterpipe smoking cessation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jun 7;6(6):CD005549. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005549.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37286509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Motivational support intervention to reduce smoking and increase physical activity in smokers not ready to quit: the TARS RCT.Health Technol Assess. 2023 Mar;27(4):1-277. doi: 10.3310/KLTG1447. Health Technol Assess. 2023. PMID: 37022933 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development of an intervention for smoking cessation in pregnant women using a theory-based approach.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Apr 25;25(1):492. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07573-5. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 40281469 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
