Atezolizumab monotherapy as first-line treatment for non-small cell lung cancer ineligible for treatment with a platinum-containing regimen (IPSOS): a cost-effectiveness analysis in the USA
- PMID: 39532375
- PMCID: PMC11574426
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-083716
Atezolizumab monotherapy as first-line treatment for non-small cell lung cancer ineligible for treatment with a platinum-containing regimen (IPSOS): a cost-effectiveness analysis in the USA
Abstract
Objective: This study explores the cost-effectiveness of atezolizumab monotherapy compared with chemotherapy as first-line treatment for stage IIIB or IV non-small cell lung cancer (IIIB/IV-NSCLC) ineligible for platinum-based chemotherapy from a US payer perspective.
Design: This is based on the IPSOS clinical trial. We conducted a comprehensive assessment of the cost-effectiveness of atezolizumab monotherapy versus single-agent chemotherapy over a 15-year duration. Employing a robust Markov model incorporating data from 453 patients, we calculated total costs, life-years (LYs), quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) and the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) at a willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold of $150 000 per QALY. We performed one-way, two-way and probabilistic sensitivity analyses to validate our model.
Setting: The US payer perspective.
Participants: A cohort with NSCLC ineligible for treatment with a platinum-containing regimen from IPSOS clinical trial.
Interventions: Atezolizumab monotherapy versus chemotherapy.
Primary outcome measure: Cost, QALYs, LYs and ICER.
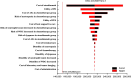
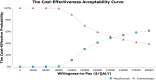
Result: Chemotherapy resulted in an average survival of 0.930 QALYs (1.528 LYs) per patient at an average cost of $67 579. Atezolizumab treatment provided an additional 0.309 QALYs but incurred an extra cost of $66 472, leading to an ICER of $215 069 per QALY compared with chemotherapy. The cost of atezolizumab had the most significant impact on the model outcomes. Probabilistic sensitivity analysis showed that atezolizumab had a 30.2% probability of being considered cost-effective at a WTP threshold of $150 000 per QALY in the USA. These results remained consistent across various scenarios and sensitivity analyses employing both deterministic and probabilistic approaches.
Conclusion: The current price of atezolizumab renders it an unlikely cost-effective treatment option for patients with IIIB/IV-NSCLC from the payer's perspective in the USA. To achieve cost-effectiveness, substantial discounts are necessary.
Trial registration number: The IMpower-110, an open-label, randomised, phase 3 clinical trial (NCT02409342). The IPSOS clinical trial (NCT03191786).
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Clinical Trial; Health Economics; Lung Diseases; Public Health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
