Comparison of drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization combined with apatinib versus drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized, prospective, multicenter phase III trial
- PMID: 39532849
- PMCID: PMC11557926
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-024-02012-x
Comparison of drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization combined with apatinib versus drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized, prospective, multicenter phase III trial
Abstract
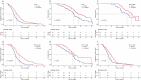
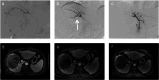
This randomized, prospective, multicenter (12 centers in China) phase III trial (Chinese Clinical Trial Registry #ChiCTR2000041170) compared drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization (DEB-TACE) combined with apatinib and DEB-TACE monotherapy for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC). Progression-free survival (PFS) was the primary endpoint. Overall survival (OS), mRECIST-based objective response rates (ORR) and disease control rates (DCR), and treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) were secondary endpoints. Totally 243 cases were randomized, with 122 and 121 in the DEB-TACE + apatinib and DEB-TACE groups, respectively. Cases administered DEB-TACE + apatinib displayed markedly improved median PFS (7.1 months [95%CI 6.6-8.3] vs. 5.2 months [95%CI 5.0-5.9]) and OS (23.3 months [95%CI 20.7-29.6] vs. 18.9 months [95%CI 17.9-20.1] compared with those treated with DEB-TACE (both p < 0.001). Additionally, patients administered DEB-TACE + apatinib had elevated ORR (56.6% vs. 38.8%) and DCR (89.3% vs. 80.2%) versus the DEB-TACE group (both p < 0.001). Majority of TRAEs were mild and manageable. Regarding DEB-TACE-related TRAEs, the rates of hepatic artery thinning and spasms were elevated during the second DEB-TACE in cases administered DEB-TACE + apatinib vs. DEB-TACE. The commonest apatinib-related TRAEs in the DEB-TACE + apatinib group included hypertension, hand-foot syndrome, fatigue, and diarrhea. In conclusion, DEB-TACE plus apatinib demonstrates superior PFS versus DEB-TACE monotherapy in uHCC cases, maintaining a favorable safety profile with similar occurrences of AEs.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines). Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Version 3.2024. Foret Washington: National Comprehensive Cancer Network; 2024.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

