METTL3 alters capping enzyme expression and its activity on ribosomal proteins
- PMID: 39532922
- PMCID: PMC11557883
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-78152-5
METTL3 alters capping enzyme expression and its activity on ribosomal proteins
Abstract
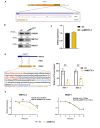
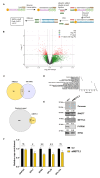
The 5' cap, catalyzed by RNA guanylyltransferase and 5'-phosphatase (RNGTT), is a vital mRNA modification for the functionality of mRNAs. mRNA capping occurs in the nucleus for the maturation of the functional mRNA and in the cytoplasm for fine-tuning gene expression. Given the fundamental importance of RNGTT in mRNA maturation and expression there is a need to further investigate the regulation of RNGTT. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is one of the most abundant RNA modifications involved in the regulation of protein translation, mRNA stability, splicing, and export. We sought to investigate whether m6A could regulate the expression and activity of RNGTT. In this short report, we demonstrated that the 3'UTR of RNGTT mRNA is methylated with m6a by the m6A writer methyltransferase 3 (METTL3). Knockdown of METTL3 resulted in reduced protein expression of RNGTT. Sequencing of capped mRNAs identified an underrepresentation of ribosomal protein mRNA overlapping with 5' terminal oligopyrimidine (TOP) mRNAs, and genes are dysregulated when cytoplasmic capping is inhibited. Pathway analysis identified disruptions in the mTOR and p70S6K pathways. A reduction in RPS6 mRNA capping, protein expression, and phosphorylation was detected with METTL3 knockdown.
Keywords: Post‐transcriptional regulation; RNA capping; RNA methylation; RNGTT; m6A; mRNA decay.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Update of
-
METTL3 alters capping enzyme expression and its activity on ribosomal proteins.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 22:2023.11.22.568301. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.22.568301. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 12;14(1):27720. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78152-5. PMID: 38045284 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

