Disease-associated B cells and immune endotypes shape adaptive immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in human SLE
- PMID: 39533072
- PMCID: PMC11695260
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-024-02010-9
Disease-associated B cells and immune endotypes shape adaptive immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in human SLE
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Disease-associated B cells and immune endotypes shape adaptive immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in human SLE.Nat Immunol. 2025 Jan;26(1):148. doi: 10.1038/s41590-024-02045-y. Nat Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39622950 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
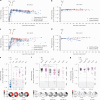
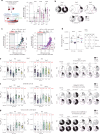
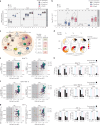
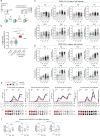
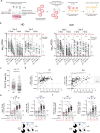
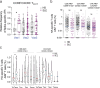
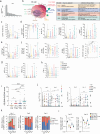
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 mRNA vaccination has reduced effectiveness in certain immunocompromised individuals. However, the cellular mechanisms underlying these defects, as well as the contribution of disease-induced cellular abnormalities, remain largely unexplored. In this study, we conducted a comprehensive serological and cellular analysis of patients with autoimmune systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who received the Wuhan-Hu-1 monovalent mRNA coronavirus disease 2019 vaccine. Our findings revealed that patients with SLE exhibited reduced avidity of anti-receptor-binding domain antibodies, leading to decreased neutralization potency and breadth. We also observed a sustained anti-spike response in IgD-CD27- 'double-negative (DN)' DN2/DN3 B cell populations persisting during memory responses and with greater representation in the SLE cohort. Additionally, patients with SLE displayed compromised anti-spike T cell immunity. Notably, low vaccine efficacy strongly correlated with higher values of a newly developed extrafollicular B and T cell score, supporting the importance of distinct B cell endotypes. Finally, we found that anti-BAFF blockade through belimumab treatment was associated with poor vaccine immunogenicity due to inhibition of naive B cell priming and an unexpected impact on circulating T follicular helper cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: F.E.-H.L. is the founder of MicroB-plex, Inc., and has research grants with Genentech. I.S. has research grants with Glaxo Smith Kline. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U19-AI110483/Division of Intramural Research, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (Division of Intramural Research of the NIAID)
- U54- 762 CA260563-01/Division of Intramural Research, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (Division of Intramural Research of the NIAID)
- GCBER008/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | U.S. Food and Drug Administration (U.S. Food & Drug Administration)
- U54 CA260563/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GCBER005/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | U.S. Food and Drug Administration (U.S. Food & Drug Administration)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

