A case of pioneering subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator intervention in Timothy syndrome
- PMID: 39533234
- PMCID: PMC11558885
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-024-05216-w
A case of pioneering subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator intervention in Timothy syndrome
Abstract
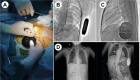
This case report presents a notable instance of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator (S-ICD) implantation in a 9-year-old patient diagnosed with Timothy syndrome (TS), which is a rare condition characterized by mutations in the CACNA1c gene. Conventional therapies often have limited efficacy in managing TS. This case is significant, as it represents the youngest age for S-ICD implantation recorded in mainland China. While the absence of ventricular arrhythmias during hospitalization and follow-up is encouraging, it is not sufficient to conclusively establish the safety and feasibility of this intervention in young TS patients. Further research is needed to evaluate the long-term outcomes and to consider S-ICD as a potential standard treatment option for TS. Additionally, there is a need for a more detailed exploration of the molecular mechanisms underlying gene therapy and personalized interventions.
Keywords: Case report; Long QT; Subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator (S-ICD); Timothy syndrome; Ventricular arrhythmias.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Clinical Outcomes and Modes of Death in Timothy Syndrome: A Multicenter International Study of a Rare Disorder.JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2018 Apr;4(4):459-466. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2017.08.007. Epub 2017 Nov 6. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2018. PMID: 30067485
-
A multicentre study of patients with Timothy syndrome.Europace. 2018 Feb 1;20(2):377-385. doi: 10.1093/europace/euw433. Europace. 2018. PMID: 28371864
-
Outcome by Sex in Patients With Long QT Syndrome With an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Oct 20;9(19):e016398. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.016398. Epub 2020 Sep 21. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 33021160 Free PMC article.
-
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, long QT syndrome, or no structural heart disease.Am Heart J. 1994 Apr;127(4 Pt 2):1151-8. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(94)90103-1. Am Heart J. 1994. PMID: 8160595 Review.
-
Is there a role for implantable cardioverter defibrillators in long QT syndrome?J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2002 Jan;13(1 Suppl):S110-3. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2002. PMID: 11852886 Review.
Cited by
-
New Machine Learning Method for Medical Image and Microarray Data Analysis for Heart Disease Classification.J Imaging Inform Med. 2025 Apr 1. doi: 10.1007/s10278-025-01492-9. Online ahead of print. J Imaging Inform Med. 2025. PMID: 40169470
-
Effectiveness of machine learning models in diagnosis of heart disease: a comparative study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 8;15(1):24568. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09423-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40629019 Free PMC article.
-
Longevity mechanisms in cardiac aging: exploring calcium dysregulation and senescence.Biogerontology. 2025 Apr 21;26(3):94. doi: 10.1007/s10522-025-10229-8. Biogerontology. 2025. PMID: 40259024 Review.
-
Cardioprotective effects of carvacrol in the isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction model.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Jul 14;26(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00967-3. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40660388 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing cardiac disease detection via a fusion of machine learning and medical imaging.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 19;15(1):26269. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12030-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40683984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shah SR, Park K, Alweis R, Long QT. Syndrome: a Comprehensive Review of the literature and current evidence. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2019;44(3). - PubMed
-
- Splawski I, Timothy KW, Sharpe LM, Decher N, Kumar P, Bloise R, Napolitano C, Schwartz PJ, Joseph RM, Condouris K, Tager-Flusberg H, Priori SG, Sanguinetti MC, Keating MT. Ca(V)1.2 calcium channel dysfunction causes a multisystem disorder including arrhythmia and autism. Cell. 2004;119(1):19–31. - PubMed
-
- Sanoudou D, Beggs AH. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity in nemaline myopathy–a disease of skeletal muscle thin filaments. Trends Mol Med. 2001;7(8):362–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- 2021SK53519/Clinical Medical Technology Innovation Guidance Project of Hunan Science and Technology Agency
- 82070356/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020SK1013/Key Project of Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Innovation
- 2021JJ30033/Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

