Predicting steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: role of lipid metabolism biomarkers and radiomics in young and middle-aged adults
- PMID: 39533346
- PMCID: PMC11558989
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-024-05245-2
Predicting steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: role of lipid metabolism biomarkers and radiomics in young and middle-aged adults
Abstract
Background: Femoral head necrosis is a common orthopedic disease that results in significant physical disability in patients. Early prediction and diagnosis of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (SONFH) are crucial for the prevention and treatment of this condition.
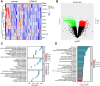
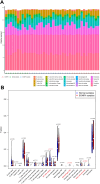
Methods: In this study, initial CT images and clinical data of patients with SONFH, admitted from January 2019 to December 2022, were collected. Patients were grouped as follows: (1) those diagnosed with SONFH at the initial diagnosis (control group), and (2) those with high-risk factors but no symptoms at first diagnosis, who developed SONFH two years later (experimental group). CT imaging histological features, clinical characteristics, and transcriptome screening for differentially expressed genes, pathway enrichment, and immune infiltration analyses were performed.
Results: Significant differences were found in triglyceride (TG) levels between the training and validation groups. Age, sex, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and hemoglobin levels differed between the training and internal validation groups, while HDL and red blood cell counts varied between the training and external validation groups. Univariate analysis showed that age, TG, HDL, and Radiomics scores influenced SONFH, while multivariate analysis revealed TG, HDL, and Radiomics scores were closely related to SONFH. Transcriptomic analysis showed associations with sphingolipid and adipocyte signaling pathways, along with immune cell involvement, linking SONFH to lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis.
Conclusions: These findings indicate a significant association between steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head and age, with TG and HDL serving as indicators of lipid metabolism closely correlated with the occurrence of SONFH. Radiomics scores were also found to correlate with SONFH occurrence, supported by transcriptomic and CT imaging findings. However, this study has limitations, including its retrospective design and a relatively limited sample size, which may impact the generalizability of the results. Further prospective studies with larger, more diverse populations are needed to validate and enhance the predictive model.
Keywords: Predictive; Preventive and personalized medicine; Radiomics; Steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Identification and analysis of mitochondria-related central genes in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head, along with drug prediction.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 7;15:1341366. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1341366. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38384969 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and validation an eight-biomarker serum gene signature for the diagnosis of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Bone. 2019 May;122:199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2019.03.008. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Bone. 2019. PMID: 30853659
-
Lipid metabolism analysis for peripheral blood in patients with alcohol-induced and steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Jul 28;47(7):872-880. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.210567. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36039583 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Pathological mechanisms and related markers of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2416070. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2416070. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39529511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pathogenesis of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A systematic review of the literature.Gene. 2018 Sep 10;671:103-109. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.05.091. Epub 2018 May 30. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29859289
Cited by
-
Cornus officinalis Protects Against Steroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head Through Inhibiting Inflammatory Responses and Apoptosis via Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jul 9;19:5871-5898. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S518115. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40661830 Free PMC article.
-
PPARγ inhibitors enhance the efficacy of statin therapy for steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by directly inhibiting apoptosis and indirectly modulating lipoprotein subfractions.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 20;20(6):e0325190. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325190. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40540523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Migliorini F, Maffulli N, Baroncini A, et al. Prognostic factors in the management of osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a systematic review. Surgeon. 2023;21(2):85–98. - PubMed
-
- Migliorini F, Maffulli N, Eschweiler J, Tingart M, Baroncini A. Core decompression isolated or combined with bone marrow-derived cell therapies for femoral head osteonecrosis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2021;21(3):423–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

