TraceEyeDisease: a web-based database for investigating trace elements and their imbalances in eye diseases
- PMID: 39533428
- PMCID: PMC11556128
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-024-06981-8
TraceEyeDisease: a web-based database for investigating trace elements and their imbalances in eye diseases
Abstract
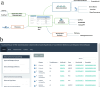
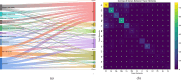
Eye diseases remain a significant global health concern, with trace elements crucial in maintaining ocular health and preventing ocular disorders. In ocular health, trace elements have been recognized as critical factors influencing the development and progression of multiple eye diseases. In this study, we conducted a thorough literature search through PubMed to acquire data concerning different eye diseases associated with trace elements. These diseases are essential in trace element imbalances or deficiencies in their progression. Our approach included a meticulous compilation of information from various databases, systematically integrated into a carefully curated database. In total, we identified 178 distinct genes that encode proteins linked to fourteen trace elements in this comprehensive list. A web-based database designed to formulate evidence-based hypotheses regarding the impact of trace element deficiency and imbalance on eye diseases was presented using Shiny R. This study underscores the vital role of trace elements in preserving ocular health. The Shiny R application facilitates subsequent investigations, fostering enhanced insights into public health, clinical practices, and eye disease research. The URL of TraceEyeDiseas is https://tredis.shinyapps.io/TraceEyeDisease/ .
Keywords: Database; Eye diseases; Shiny R; Trace elements.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glaucoma-TrEl: A web-based interactive database to build evidence-based hypotheses on the role of trace elements in glaucoma.BMC Res Notes. 2022 Nov 18;15(1):348. doi: 10.1186/s13104-022-06210-0. BMC Res Notes. 2022. PMID: 36401306 Free PMC article.
-
Recent insights into trace element deficiencies: causes, recognition and correction.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2020 Mar;36(2):110-117. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000612. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 31895229 Review.
-
CBPDdb: a curated database of compounds derived from Coumarin-Benzothiazole-Pyrazole.Database (Oxford). 2023 Sep 13;2023:baad062. doi: 10.1093/database/baad062. Database (Oxford). 2023. PMID: 37702993 Free PMC article.
-
Benefits and risks of essential trace elements in chronic kidney disease: a narrative review.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Dec;10(24):1400. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5969. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36660676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The essential trace elements.Science. 1981 Sep 18;213(4514):1332-8. doi: 10.1126/science.7022654. Science. 1981. PMID: 7022654 Review.
References
-
- Health NRC, editor. C on D and. Trace Elements. Diet and Health: implications for reducing Chronic Disease Risk. National Academies Press (US); 1989. - PubMed
-
- Bunce GE. Trace element and Mineral Nutrition in diseases of the Eye. In: Bogden JD, Klevay LM, editors. Clinical Nutrition of the essential Trace Elements and minerals: the Guide for Health professionals. Totowa, NJ: Humana; 2000. pp. 371–80.
-
- Karcioglu ZA. Zinc in the eye. Surv Ophthalmol. 1982;27:114–22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

